Meniscus Tears And Pain Behind Your Knee
Root tearsof the meniscus are prevalent. The root of a meniscus is where the meniscus attaches to the shin bone or tibia. Much like a tree roots into the ground, the meniscus has a firm, deep attachment to your bones as well.
Sadly, over the years, these attachment points or roots can weaken. A common story is that you bent down or knelt and felt a pop in the back of the knee. Later that day or two days later, your knee is swollen, and the pain is very severe. The root of the meniscus tore in this situation because it had degenerated from decades of activity.
The pain from root tears often subsides over the next few weeks to months. By the time you see a doctor, and they order an MRI, the pain is often starting to improve. This post below goes into far more detail about root tears as the cause of pain in the back of your knee.
The meniscus is a shock absorber. When the root of the meniscus tears, the meniscus no longer works as a shock absorber. Therefore, following a root tear, you may develop stress fractures or stress reactions. That is why the pain worsens a few days after you felt the pop.
On some occasions, we need to consider surgery to repair these root tears but this is not usually necessary.
What Is A Popliteus Injury
The Popliteus muscle is responsible for internal rotation of the shin bone. It is also the muscle used when you unlock your knee from a straight position. Injury of the popliteus muscle can be either from an acute injury or through overuse.
Acute popliteus injuries
Acute injuries to the popliteus occur after a significant force to the knee. They are common in road traffic accidents or falls where the knee is extended or over straightened. It might also be injured through impacts which force the knee out to the side.
Popliteus injuries may occur in associated with other injuries such as posterior cruciate ligament tears or occasionally ACL ruptures, as well as being part of the posterolateral corner injury involving a number of other structures in the knee.
Overuse injuries
Overuse injuries to the popliteus muscle develop gradually and are most common running injuries. They tend to be due to biomechanical issues and tight hamstring muscles are often partly to blame.
Lower Back And Knee Pain Relationship
There are many possible reasons why lumbar symptoms can be related to pain in the knees. If a spinal issue causes the patient to favor one side, or move in an unusual manner, the knee may suffer stress leading to painful symptoms. Likewise, if the knee has an injury or degenerative condition which causes the patient to hold all their weight on one side, the spine may suffer some pain, as well.
These are the normal working theories used to explain combination pain in both locations, according to the Cartesian medical model. These have also been the ideas of pain championed by many physical therapists and chiropractors over the years. In some scenarios, these theories are correct, but in many cases, they completely miss the point. This has been supported by the widespread propagation of the idea that most structural findings on MRI, in the knee or back, do not correlate to the incidence, location or severity of pain.
You May Like: Are Epidural Injections For Back Pain Safe
I Have Just Injured My Leg And Have Severe Pain At The Back Of My Knee What Should I Do
A sudden, sharp, pain in the thigh or behind the knee may be a torn hamstring, or possibly a tear in the posterior part of the meniscus. Alternatively, if you have sudden pain and instability after an injury, perhaps accompanied by a popping sound, you may have damaged a knee ligament. It could also be a ruptured Bakers cyst. In these cases, whilst RICE is recommended initially, you should go to your doctor and have the knee clinically assessed.
Possible Causes Of Pain
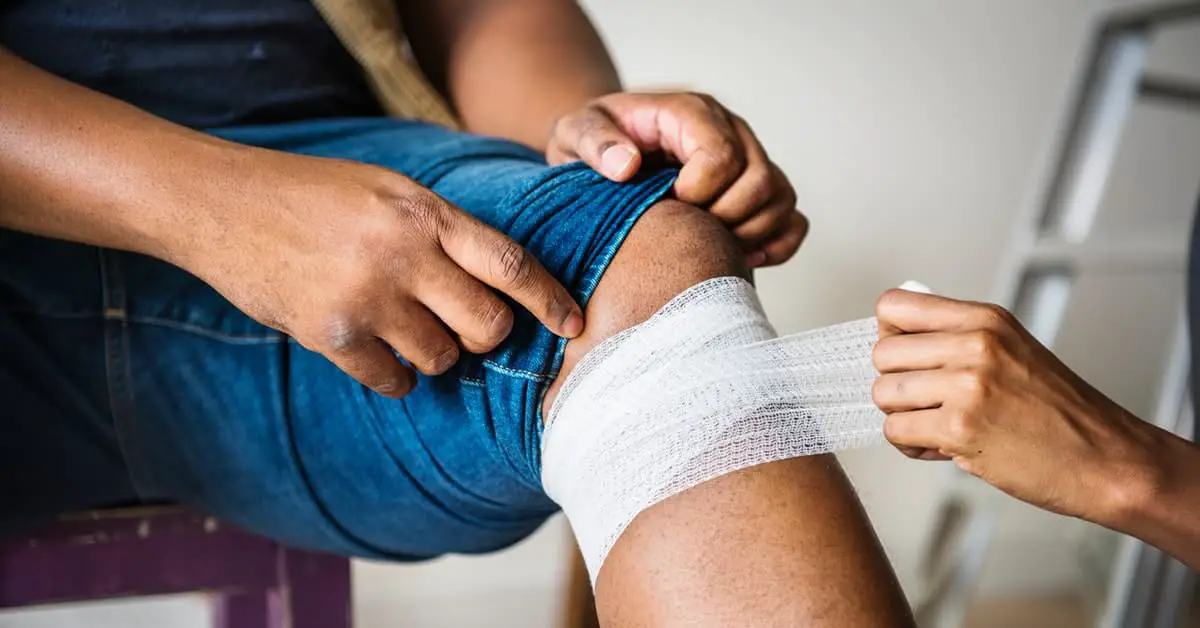
Quadriceps tendonitis this is caused by the irritation, strain or injury to the quadriceps tendon.
Patellofemoral Arthritis
This affects the underside of the kneecap and the trochlear groove in the femur in which it moves. When the articular cartilage covering the surfaces of the bone wears away and becomes inflamed the bones come into contact with each other resulting in pain.
Plica Syndrome
A plica is the fold in the thin synovial membrane that lines the knee joint. There were four of these folds in the knee joint originally, but they often become absorbed during foetal development. About 50% of the population is thought to have the remains of the embryonic plicae. When a plica becomes inflamed, perhaps because of repetitive knee movement, trauma or twisting, it causes pain and weakness in the knee.
Lateral patellar facet overload syndrome
This refers to dull aching pain underneath, around the sides or below kneecap. It is caused by increased pressure on the lateral facet of the patella. The reason for this is improper tracking, poor alignment or dislocation of the kneecap. The condition is often apparent during repetitive exercise such as climbing stairs.
Synovitis
Read Also: What To Do To Alleviate Lower Back Pain
Muscle And Tendon Conditions
The shallow depression formed at the back of the knee is called the popliteal fossa it is formed at the junction of the femur and tibia. There is a muscle here on the floor of the popliteal fossa which is the deepest muscle of the knee joint. It works on the femur to rotate it on the tibia when walking. Through the popliteal depression a bundle of muscles run from the pelvis to the knee and attach to the tibia and fibula respectively by tendons. These three muscles are collectively called the hamstring muscles, and function to extend the leg and bend the knee.
At the back of the lower leg the calf muscles are composed of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles which flex the leg at the knee and flex the ankle via the achilles tendon.
Bakers Cyst And Pain In The Back Of The Knee
A Bakers cyst is a fluid-filled pocket in the back of the knee. Bakers cysts are a common cause of painful swelling. If the cysts are small, they do not create much discomfort.
A Bakers cyst can grow larger. If a cyst becomes large, it can put pressure on the muscles, blood vessels, and nerves behind the knee and can cause discomfort. Most people with a Bakers Cyst will also have osteoarthritis.
In most instances, treatments to diminish the swelling associated with arthritis will help reduce the pain and swelling from the cyst. In the majority of cases, these cysts are not dangerous. An ultrasound can usually tell if you have a simple cyst versus something more complex that warrants further evaluation with an MRI. If the Bakers cysts are huge, then one treatment alternative is to have the fluid drained. While that will result in relief of pain, the fluid might come back again.
Read more about a Bakers cyst.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Mattress Is Best For Back Pain
What Should I Do If I’m Experiencing Pain At The Back Of My Knee
If you are dealing with back-of-knee pain, Dr. James makes the point that it is imperative to “see your healthcare provider to rule out some of these more serious causes.” Dr. Holder agrees, recommending a “clinical assessment of the knee is comprehensive and includes for instability, edema, and clicking or popping along with pain.” Dr. James mentions that if the diagnosis is related to overuse or muscle imbalances like tendonitis or bursitis, an exercise regimen that “focuses on proper form, good posture, and rebalancing the muscles around the knee” would be very helpful. Whether the pain is due to something more serious or not, Dr. Holder asserts that an orthopedic assessment and a physician evaluation are crucial to providing an accurate diagnosis, and that it’s important to get treatment as soon as possible.
Burning Pain When Sitting Still
Some people feel more pain at night than during the day.
You might feel more pain when you’re sitting still. Some of us are just too busy to monitor pain. We need debilitating pain to tell us to slow down and be still.
So when you sit down and take a break, do not be surprised if the little niggles of pain begin to visit you.
Your nightly knee pain can also come from reduced hormone signals. When you rest, your hormone signals are reduced. These reduced hormone signals give way for pain signals to reach the brain.
So you’ll feel pain as you try to nod off.
Your blood vessels may also be the culprit for pain at night. When you sleep, your blood vessels increase in diameter. This is a natural process that allows more blood to come to muscles, allowing them to heal.
However, those expanding blood vessels can put pressure on your nerves. This will cause pain such as pain in your knee even as you try to sleep.
Don’t Miss: How To Remedy Lower Back Pain
What Are The Symptoms Of Patellar Tendonitis
Pain and tenderness at the base of your kneecap are usually the first symptoms of patellar tendonitis. You may also have some swelling and a burning feeling in the kneecap. Kneeling down or getting up from a squat can be especially painful.
The pain may at first be sporadic, occurring only after sports or exercise activity. As the tendon becomes more damaged, the pain can become progressively worse. It can interfere with any athletic activity, as well as with daily activities, such as climbing stairs or sitting in a car.
See your doctor if any pain or swelling lasts more than a day or two.
At the start of your appointment, your doctor will ask about:
- your physical activity
- what symptoms youre experiencing
- when the symptoms occur
- any remedy youve tried that eases the pain
Your doctor will physically examine your knee, probe for where you feel pain, and test your range of knee motion by bending and extending your leg.
Your doctor may also order imaging tests to look at your kneecap and tendon to determine if theres any damage to the tendon or bone. These tests can also help rule out other possible causes of your pain, such as a fracture.
Your doctor may perform:
- an X-ray to look at the bone to determine whether you have a kneecap fracture or if your kneecap is displaced
- an MRI to look at the tendon and show any damage to the soft tissue
- an ultrasound to look at the tendon and show any soft tissue damage
When To See Your Doctor
Don’t wait if your knee pain is sudden and intense. Pick up the phone if it won’t go away or gets worse.
To make a diagnosis, your doctor might take X-rays or other images of your knee. Blood or knee fluid samples can help confirm or rule out certain conditions. Treatment may include medication, special exercises, braces, or in some cases surgery. Losing weight could help lessen pressure and strain on your knees.
Recommended Reading: How To Relieve Back Pain From Standing All Day
Pain Behind The Knee When Bending It Or Pain And Stiffness Below The Kneecap
Although not behind the knee, the patellar tendon can be overloaded and torn by repetitive actions such as jumping, running or kicking. This is called patellar tendonitis, and can get progressively worse as the the torn tendon swells and becomes weaker. Again the RICE formula should be applied, and your doctor should be consulted.
Q: What Foods Do You Recommend I Eator Avoid
JD: Id look first at the types of fats youre eating. Chronic inflammatory pain is a sign that you have higher-than-normal levels of pro-inflammatory prostaglandins. Prostaglandins, a kind of hormone, come in two types: One encourages inflammation, while the other inhibits it. Because both are constructed from fatty acids, the kind of prostaglandins that predominate in your body depends partly on the kinds of fats you eat.
Youll want to stay away from pro-inflammatory fats, such as butter, whole milk, margarine, corn oil, sesame oil, coconut oil, and vegetable shortening. And steer clear of trans fats, which are often found in processed foods. At the same time, increase your intake of anti-inflammatory omega-3 oils. Good sources include salmon, herring, mackerel, flaxseed oil, and walnuts.
Finally, make sure youre getting five to six servings of fresh fruits and vegetables a day and substituting whole grains for white bread and rice. A healthy diet will also help you lose weight.
Read Also: How To Correct Back Pain
How Is Knee Pain In Teens Treated
Treatments depend on the cause of your teens pain.
Pain from overuse and general knee pain management tips include:
- Apply ice to the knee. Ice, wrapped in a towel, relieves inflammation and swelling. Apply up to 20 minutes at a time.
- Take anti-inflammatories, such as ibuprofen , naproxen or aspirin, to reduce pain and swelling.
- Rest. Rest allows tissue to heal. Your teen should take some time off from the activity that caused the pain.
- Use compression around your knee if prescribed by your healthcare provider or physical therapist.
- Elevate the knee to reduce swelling. Keep the injured knee elevated above the level of the heart anytime your teen is sitting or icing their knee.
- Follow through with the physical therapy plan. Physical therapy can help relieve pain, reduce swelling, increase strength and flexibility, improve range of motion, increase speed and endurance and improve coordination and balance. Physical therapists teach strengthening and stretching exercises and can suggest braces, insoles or other orthotics as appropriate.
- Lose weight if overweight. Extra weight puts strain on the knee joint.
Osgood-Schlatter disease:
- Take anti-inflammatories to reduce pain.
- Apply ice to reduce pain and swelling.
- Commit to an exercise program.
- Relieve pain and discomfort through electrotherapy and/or hydrotherapy .
Sindling-Larsen Johansson syndrome:
- Soft tissue treatments, including myofascial release, trigger points, massage.
Ligament treatment:
Is Pain Behind The Knee A Blood Clot
One of the causes of posterior knee pain is DVT. If you have incurred a fracture, severe muscle injury, or have gone through major surgery, the vein at the back of your leg may be injured. A direct injury to the vein can result in DVT, where a clot forms at the back of the leg. DVT can also be caused by prolonged bed rest, immobilizing the leg through casting or bracing, leg paralysis, or blood disorders.
If you feel deep, throbbing pain at the back of the leg, accompanied by swelling, redness, and warmth in the surrounding skin, you must call your doctor immediately as DVT is a condition that can cause serious complications.
Recommended Reading: How To Relieve A Lower Back Strain
Common Causes Of Sharp Knee Pain
The most common causes of sharp knee pain are:
- Torn Knee Cartilage: the special cushioning the lines the knee joint
- Knee Bursitis: inflammation of anti-friction sac
- Knee Arthritis: wear and tear
- Loose Body: bone fragment floating in the joint
- Fracture: broken bone
- Nerve Irritation: nerve gets squashed or irritated
Here we will look at the common causes of sharp knee pain, how they present and how to work out what is going on in your knee. We then look more in-depth at how to treat these different causes of sharp pain in the knee.
Who Gets Pain In The Back Of The Knee
Pain behind the knee is most often found in adults as a result of wear and tear from daily activities such as walking, standing, bending, and lifting. Additionally, athletes who run and engage in sports that involve running, jumping, and quick pivoting of the knee may experience this type of knee pain. It is important to seek medical attention for any acute and/or long-term knee pain you may be experiencing.
Read Also: What Causes Upper Left Back Pain Under Shoulder Blade
Lower Back And Knee Facts
The sciatic nerve is responsible for providing neurological signals to much of the lower anatomy, including the knee. The nerve roots which compose the sciatic are sourced in the lumbar spinal region. Therefore, there can certainly be a spinal relationship which causes pain in the back and sciatica symptoms in the legs, including the knee. This is also a very common diagnostic theory and is sometimes accurate. I suffer from this combination myself .
However, ischemia is known to attack the soft tissues and nerves in the back as one of its favorite targets. Ischemia can cause widespread and severe back pain and the effect on the sciatic nerve and its peripheral branches can cause chronic knee pain, as well. Dr. Sarno speaks of this combination of symptoms existing in many patients, either in successive bouts or even concurrently with one another.
Lower Back and Knee Pain Analysis
If there is no obvious injury or functionality concern causing the pain, then something else must be responsible. In most cases, spinal MRI will turn up some structural condition in the lumbosacral region to blame the pain upon. This is simply due to the universality of arthritis and disc desiccation in the region and the virtual universality of herniated discs. In the majority of cases, this diagnostic therapy turns out to be unenlightened and downright incorrect. The abysmal curative results offered by most back pain treatments and many knee surgeries support this fact 100%.
Whilst Squatting With A Heavy Load I Heard A Pop And Experienced Sudden Pain Should I Go To My Gp
A popping or cracking sound on its own is not unusual and nothing to be worried about. However, if accompanied by sudden pain you may have damaged one of your knee ligaments , or torn a meniscus. You should consult your doctor. If the problem does not clear up I would be happy to see you and assess things further.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Chronic Lower Back Pain