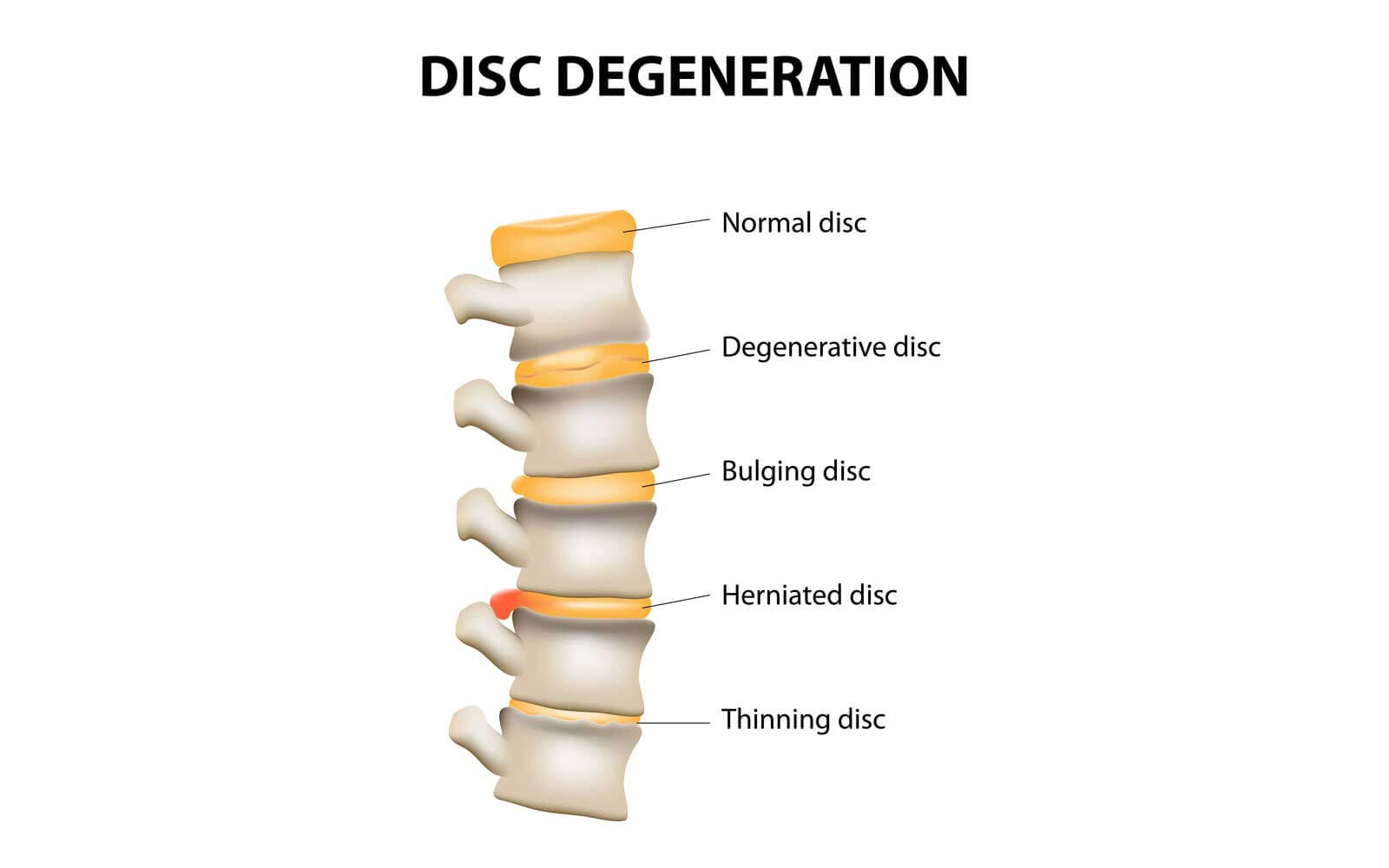
Signs And Symptoms Of Degenerative Disc Disease
How can you tell if you have degenerative disc disease?
There are a few symptoms you need to look out for. Mostly, youll start to feel pain somewhere in your back, and where you feel the pain in your back will depend on which disc has suffered damage. For example, you could feel pain in your buttocks, upper thighs, lower back or further up even into your neck.
The pain may be sharp, or nagging. Itll come and go, and feel better when you get up and move around. Itll feel worse when youre sitting. Itll also feel worse when you bend and twist.
As well as pain, you may experience numbness and tingling in your arms and legs. Many people worry, thinking degenerative disc disease can cause you to become paralyzed. In rare cases, it can happen. However, most often, degenerative disc disease surgery can be carried out to prevent this, so youll probably never have to deal with paralysis becoming a problem.
Can you die from degenerative disc disease?
Although the diagnosis can sound frightening, you dont need to panic. You certainly cannot die of a degenerative disorder such as this one.
Spinal Fusion For Degenerative Disc Disease
During a spinal fusion surgery, two adjacent vertebrae are grafted together to alter the underlying mechanisms causing pain. A fused joint eliminates instability at a spinal segment, reducing pain caused by micro-motions, muscle tension, and/or inflammation. Joint fusion can also allow for a more thorough decompression of pinched nerves.
A spinal fusion procedure typically consists of the following steps:
- Under general anesthesia, an incision is made to approach the spine. For a cervical fusion, the incision is usually made in the front of the neck. For a lumbar fusion, an incision may be made in the back, front, or side of the body.
- Muscles surrounding the spine are cut away or pushed to the sides to access the spine.
- The degenerating disc is removed from the disc space.
- A bone graft and/or instruments are implanted across the disc space to stabilize the spinal segment and encourage bone growth.
- The spinal muscles are replaced or reattached, and the incision site is closed with sutures.
A fusion surgery sets up the mechanisms for bone growth, and the fusion occurs in the months following the procedure. For this reason, the complete recovery process from a fusion surgery can last up to a year, although a majority of patients are back to their regular activities within six weeks.
Diagnostic Imaging For Degenerative Disc Disease
A definitive diagnosis for lumbar DDD may require an MRI scan to ensure that other issues are not contributing to pain, such as a fracture or disc herniation. If surgery is needed, an imaging test is required prior to the procedure to accurately locate the degenerated disc and plan the surgery.
An MRI scan uses a high-powered magnet to align and detect water molecules in the body, which allows doctors to visualize soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments and tendons, and spinal discs. MRI scans rely on magnetism rather than radiationused in x-ray and CT scansso there is little risk involved in an MRI scan, and scans are not painful.
MRI scans can provide useful information concerning:
- Disc height
- Endplate erosion
- Pinched nerves
- Disc hydration
Studies have shown that MRI findings of mild or significant disc degeneration are found on scans of patients with severe pain and minimal or no pain. Additionally, many painful conditions may not show up on an MRI, such as a tear in the discs outer rings or some cases of herniated discs. For this reason, a diagnosis cannot rely solely on imaging tests and must be used in combination with a medical history and physical examination.
Pain from degenerative disc disease is typically caused by strain on the muscles supporting the spine and inflammation around the disc space.
Don’t Miss: What Doctor To See For Back And Leg Pain
Degenerative Disc Disease Symptoms & Treatment
Spinal discs, discs in between the bones that make up your spine , allow your back to bend and twist flexibly. They act like shock absorbers, insulating against impact. In the course of day-to-day life, these discs take on a great deal of strain. As a result, these discs can eventually start to break down and cause pain leading to a condition called degenerative disc disease , or cervical disc disease.
Your spine is divided into regions:
- Neck or upper back
- Middle-back
- Lower back
Disc degeneration most commonly occurs in the upper and lower regions.
Unfortunately, since invertebral discs receive less blood flow than other soft tissue, the damage doesnt heal well on its own. In some cases, these deteriorated discs may collapse and cause the joints in the vertebrae to rub against each other, which can cause spinal osteoarthritis, characterized by stiffness and pain of the joints.
Aurora offers a variety of disc degeneration treatments including surgical and nonsurgical approaches.
Do I Need Surgery For Degenerative Disk Disease
Many patients do not need surgery for degenerative disk disease. But if you have tried multiple nonsurgical treatments and have persistent pain and/or weakness, surgery may be a good option.
Or your surgeon may use one of a few types of spinal decompression surgery:
- Diskectomy: Removing part of a spinal disk to relieve pressure on your nerves.
- Foraminotomy: Expanding the opening for your nerve roots by removing tissue and bone.
- Laminectomy: Taking out a small portion of bone from your lower spine .
- Osteophyte removal: Removing bone spurs .
- Spinal fusion: During this procedure, your surgeon connects two or more vertebrae to improve stability.
Read Also: Should You Go To Urgent Care For Back Pain
When Is Surgery Indicated For A Disc Problem
Acute discs typically get better with rest. The only absolute indication for surgery is if the disc is so large that it suddenly causes bowel or bladder problems. In that case, the surgery should be done right away to prevent permanent damage to those nerves. If the disc is in the neck and the legs are suddenly affected, some physicians would consider an operation necessary right away.
Some physicians may also consider surgery if the symptoms of weakness in the extremities are progressing at a rapid rate. In a vast majority of cases, immediate surgery is not indicated. Because up to 98 percent of disc problems get better without surgery, it is not needed if the symptoms can be controlled. Tingling and numbness get better in most cases, and weakness in the muscles may take longer to recover. Some patients have recurrent bouts of back pain with or without nerve involvement. Sometimes these happen frequently and keep the person out of work, out of their sport or generally restricted from their activities. In those cases, injection of steroids into the area around the disc can sometimes get rid of the pain and inflammation. If that does not help, then surgery is an option.
Example Progression Of Treatment Regimens For Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Treatments need to be individualized. However, as a general rule, lumbar degenerative disc disease treatments start with basic pain control and non-invasive treatments and progress, if needed, to more extensive and/or invasive treatments.
One example of how treatment approaches may progress over time would be:
- Bed rest, or reduced activity, for the first 1 to 2 days after onset of severe pain, combined with anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen, and ice and/or heat therapy
- Prescription muscle relaxant medications, as needed, for up to 1 week
- Gentle stretching and aerobic exercise, for at least 3 times a week
- Physical therapy if after 3 weeks there is no improvement in pain
- An epidural injection if after 3 to 6 weeks there is little to no improvement in pain
- Spinal surgery if after 6 to 12 months the pain is severe, ongoing and significantly limits daily activities
Bed rest beyond the first 2 days of sharp, severe pain is not usually advised, because regular movement improves blood circulation and muscle strength and helps the body to heal more quickly than bed rest.
The above is just one example of a typical progression of treatments, and additional therapies or a different type of progression of care is not uncommon based on the patientâs condition and the treating physicianâs preferences as well as other variables.
Recommended Reading: What To Do For Arthritis Pain In Lower Back
What Are The Symptoms Of Degenerative Disc Disease
| Degenerative disc disease refers to a condition in which pain is caused from a damaged disc. The X-ray shows degenerated discs on the left before surgery. On the right is an X-ray of the discs after traditional spinal fusion surgery. |
The typical person with degenerative disc disease is active, otherwise healthy and in his or her 30s or 40s.
Common symptoms of this condition include:
- Pain that is worse when sitting. While seated, the discs of the lower back have three times more load on them than when standing.
- Pain that gets worse when bending, lifting or twisting.
- Feeling better while walking or even running than while sitting or standing for long periods of time.
- Feeling better changing positions often or lying down.
- Periods of severe pain that come and go. These last from a few days to a few months before getting better. They can range from nagging pain to disabling pain. Pain can affect the low back, buttocks and thighs or the neck, depending on where the affected disc is, radiating to the arms and hands.
- Numbness and tingling in the extremities.
- Weakness in the leg muscles or foot drop, a possible sign of damage to the nerve root.
What Is The Outlook For People With Degenerative Disk Disease
Many people use nonsurgical and at-home treatments to manage pain long-term. If you have mild to moderate back pain, you will need to continue treatment to keep the pain at bay.
Most people who have surgery for degenerative disk disease experience long-term pain relief. Even after surgery, you need to continue exercising and stretching to keep your back strong and healthy.
Read Also: Which Food Is Not Good For Back Pain
Diagnosis For Degenerative Disc Disease
Your doctor will take your medical history, a list of your symptoms, and perform a physical exam to check your muscles, nerves, pain, and mobility.
You may need some imaging tests like x-rays, magnetic resonance imaging , or computed tomography scan to see your spine and discs. They will check the structure of your spine and look at if your discs are collapsing or if you have bony projections on the joints called bone spurs.
What Are The Causes
In addition to age and injury, arthritis and osteoporosis contribute to disc degeneration.
Most disc abnormalities can be seen on an MRI scan. While a large portion of people with back pain have abnormalities confirmed by MRI, studies on healthy young adults have shown that as many as 30% of people without pain also have abnormalities that can be seen on an MRI scan.
Its not known why some people have pain and others dont, but various factors contribute to disc degeneration including: genetic, environmental, autoimmune, inflammatory, and traumatic factors in combinations that arent yet understood.
Also Check: How To Stop Back Pain At Night
Risk Factors For Degenerative Disc Disease
Lifestyle factors that affect overall health can have an impact on the spinal discs. Risk factors for degenerative disc disease include:
- Family history of back pain or musculoskeletal disorders
- Excessive strain on the low back caused by sports, frequent heavy lifting, or labor-intensive jobs
- Strain on the lumbar spinal discs due to prolonged sitting and/or poor posture
- Lack of support for the discs due to weak core muscles
- Obesity
- Smoking, or any form of nicotine intake
Disc degeneration is a common part of aging, but not all people develop pain or any remarkable symptoms. Symptoms tend to arise when spinal instability, muscle tension, and possibly nerve root irritation occurs.
Most cases of lumbar degenerative disc disease consist of a low-grade, continuous but tolerable back pain that will occasionally intensify for a few days or more.
Symptoms can vary, but general characteristics usually include:
Disc degeneration should not cause symptoms of bowel/bladder dysfunction, fever with back pain, unexplained and rapid weight loss, or intense stomach pain. These symptoms are suggestive of more serious conditions and should receive prompt medical attention.
Steroid Injections By A Doctor
If your pain is non-responsive to these methods, or if youre in so much agony you cant begin an exercise program, epidural steroid injections into the area round your facet joints may help.
An estimated half of patients who receive corticosteroid injections report significant relief of their pain symptoms.
Steroid injections are not a first-line approach. Theyre not guaranteed to work and they can not be repeated often because shots administered to the same location over time can promote bleeding and bruising. Steroids can also have a negative effect on surrounding tissue. Doctors advise no more than three injections per year.
You May Like: Why Do I Always Have Back Pain
How Is A Diagnosis Made
When you first experience pain, consult your family doctor. Your doctor will take a complete medical history to understand your symptoms, any prior injuries or conditions, and determine whether any lifestyle habits are causing the pain. Next a physical exam is performed to determine the source of the pain and test for any muscle weakness or numbness.
Your doctor may order one or more imaging studies: X-ray, MRI scan, discogram, myelogram, or CT scan to identify a herniated disc or other conditions that compress the nerve roots. Based on the results, you may be referred to a neurologist, orthopedist, or neurosurgeon for treatment.
Diagnosing Degenerative Disc Disease
Diagnosis of degenerative disc disease is made through a detailed history and physical exam. There are many tests that can aid in the diagnosis which include MRI scan, x-rays, CT scan, and discography. Your spine specialist will decide which tests are necessary based on the history, physical examination, and test done to date.
Read Also: Can Sitting Cause Lower Back Pain
Red Flags That May Point To A Need For Spine Surgery
- Lumbar herniation causing loss of bowel or bladder control, or major lower extremity deficit, requires immediate surgery. These symptoms are caused by nerve root compression.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome is a serious disorder that may be caused by a large central herniation. The cauda equina begins at the end of the spinal cord. The cauda sac is filled with nerves resembling the tail of a horse. When this sac is compressed the patient may present with the following symptoms: low back pain, bilateral lower extremity weakness, radiculopathy , and incontinence.
When these symptoms present, surgery is required immediately. Most herniated discs often do not require surgical intervention and respond quite nicely to non-surgical treatments .
Can Spinal Disc Disease Heal On Its Own
First of all:
Just because DDD includes the word degenerative in it, doesnt mean that your symptoms will get worse.
While its true that disc degeneration may progress over time, the pain you are experiencing can be dramatically reduced and even eliminated, especially if you help your body using the natural methods listed here.
You can not really reverse DDD but you can make lifestyle changes that can protect your spine and keep it from getting a lot worse.
A few other lifestyle changes can have a powerful healing effect on your back pain:
1. If your work requires sitting for long periods of time, consider switching your office chair to a balance ball chair.
2. Learn how to fix your posture, which is incredibly important for managing lower back pain.
3. Modify your sleep position to avoid pressure on your spine when you sleep. A good body pillow can turn around your sleeping experience forever.
Recovering from degenerative disc disease in the lower back requires combining a few natural and remarkable effective natural treatments.
In this post, youve learned about home back traction, DDD exercises, infrared heat, anti-inflammation food and supplements, back braces, and self-massage tools.
It may take some dedication and time, but it wont cost your life savings and you wont depend on lifetime pain killers and possible surgery.
Natural treatments for low back degenerative discs can be fabulously effective, all you need is to get up and give them a try.
Meital
References
Recommended Reading: Can Acupuncture Help Lower Back Pain
What Are The Symptoms
You’ll probably feel a sharp or constant pain in your back and neck. Your exact symptoms depend on where the weak disk is and other changes it has caused.
Common signs include pain that:
- Is in your lower back, buttocks, or upper thighs
- Comes and goes. It can be nagging or severe, and can last from a few days to a few months.
- Feels worse when you sit, and better when you move and walk
- Feels worse when you bend, lift, or twist
- Gets better when you change positions or lie down
In some cases, degenerative disk disease can lead to numbness and tingling in your arms and legs. It can also cause your leg muscles to become weak. This means the damaged disks may be affecting the nerves near your spine.
How To Treat Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease describes a group of symptoms that results from age-related wear-and-tear of the spinal discs. It could also be a result of an acute spinal injury that causes the spinal column to deteriorate or break down.
Despite its name, degenerative disc disease is, in fact, not a disease. This is a natural occurrence that is a result of aging. The rubber-like discs between the vertebrae that act like shock absorbers allow for bending and flexing of the back. Overtime, they become worn out and are unable to provide the highest level of protection. MRIs show some kind of deterioration of the spine in the majority of patients over the age of 60.
Don’t Miss: How To Fix Lower Back Pain Quickly