Contact Disc For A Consultation Today
Smoking and chronic pain have what some researchers call a comorbid relationship. Pain can lead people to begin smoking and may be similar to what they feel later in life because of smoking. This cycle can cause irreversible damage to your spine.
Chronic back pain is a prevalent condition that affects millions of adults. Its worst cases can prevent you from enjoying many simple pleasures of life. At Desert Institute for Spine Care, we treat hundreds of patients with chronic back pain. Our personalized diagnostic approach finds the source of your pain and helps you address solutions or appropriate treatment.
If you smoke and have noticed symptoms of chronic back pain, our specialists can help you identify solutions. We begin with the root and create an individualized plan to help you feel better. We start with minimally-invasive treatments, such as medication or therapeutic injections, but can also perform innovative surgical procedures.
DISC specialists are Arizonas leaders in minimally invasive spine care. Our procedures range from traditional treatments to complex spine surgery. We will always recommend the least invasive option to alleviate your pain. If you want to know more about our services, you can contact us online. Call 602-944-2900 if you have questions.
Smoking Affects Blood Flow
A common compound found in cigarettes is nicotine which narrows your blood vessels and limits the amount of blood reaching your systems and organs. Narrow blood vessels also decrease the amount of oxygen and nutrients your cells receive. This can end up damaging your ligaments and muscles located in the spine area, which can then lead to back pain. Pay attention to all your symptoms aside from low back pain. This is necessary to help you find an efficient remedy if needed.
Smokers and those exposed to smokers regularly are also at risk for atherosclerosis. This condition leads to a decreased blood flow to your organs and body tissues which may then result in ischemia which can potentially cause low back pain and even intervertebral disc degeneration.
Mechanism Of Nicotine Action
A variety of factors are believed to contribute to the analgesic effects of short-term exposure to nicotine.
First, nicotine is an agonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors , which are found throughout the peripheral and central nervous system, and notably in brain regions associated with pain transmission, such as the dorsal horn, locus ceruleus, and thalamus. Specifically, nicotine acts on the 34 ganglion type in the autonomic ganglia and adrenal medulla, and the 42 nicotinic receptors in the central nervous system. The increased binding of nAChRs produces central antinociceptive effects that activate the spinal cord descending pain-inhibitory pathways, resulting in discharge of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla and catecholamines from sympathetic nerve endings.¹
Activation of nAChRs also potentiates the release of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, that play a role in nicotine-mediated analgesia.¹¹ This increased stimulation of dopamine also activates the mesolimbic dopamine reward system, which increases the importance of incentive cues associated with nicotine use. Through this reward system, painful stimuli can become a conditioned cue for smoking. Interestingly, activation of nAChRs is similar to activation of opioid receptors in that both stimulate the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, which mediates the rewarding effects of nicotine and plays a role in pain perception.¹²¹³
Recommended Reading: Can A Broken Rib Cause Back Pain
Smoking And Neck Pain
Some smokers experience pain in the right side of the neck after smoking, as well as generalised neck pain.
The cervical spine is the neck region of the spinal bone. It consists of vertebrae with cervical discs in between them that absorb shock sustained by the spine.
Smoking can damage the cervical discs in the neck. These discs naturally become dehydrated and shrink as we age, but smoking accelerates this wear and tear.
This occurs because the nicotine within tobacco increases the risk of microvascular disease, which is disease of the small blood vessels.
The intervertebral discs source nutrition from the microvasculature that lines both sides of the disc. If the blood vessels become injured due to smoking, the discs cannot be nourished properly, which leads to disc degeneration.
A study has shown that current smokers had more severe cervical degenerative disc disease than non-smokers.
Another study found that smoking increases the rate at which the cervical discs degenerate, leading patients to present with more severe neck and shoulder pain.
How Smoking Affects The Backs Ability To Heal

Some active smokers will recognize intense lower back pain and assume the damage has been done. Fortunately, you can alleviate your back pain and mitigate the risks of further spinal degeneration. The best way to begin healing is to stop or significantly reduce smoking.
Recovering from chronic back pain may involve any range of physical therapies, surgeries or habit changes. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your body. Researchers have found that smoking cessation can improve spine health and reduce the risk of diseases like sciatica. You may see excellent progress without surgery when you quit smoking.
Your chronic pain recovery begins when you get rid of the toxic substance that has weakened your body over time. Studies have found that smoking can increase your pain sensitivity, meaning your chronic back pain may feel worse because you smoke. In turn, you may feel less pain once you quit smoking and speak with a specialist about your lower back pain.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Relief From Upper Back Pain
What To Do About Chronic Upper Back Pain After Smoking Cessation
Dr. Vilma received her M.D. from Harvard. Her practice includes areas specific to the health of women of all ages as well as general health and prevention issues.
Learn about our Editorial Policy.
For most people, smoking cessation improves back pain or makes it easier to treat. However, some people complain of increased pain after quitting smoking. If you develop acute or chronic upper back pain after smoking cessation, there are a number of remedies that can help diminish musculoskeletal pain. If there is no improvement, see your doctor to rule out other causes of your back pain such as lung disease related to your smoking, as well as for additional treatment.
Smoking Hurts Your Spine
The disks of the spine, which provide cushion to the spine and offer ranges of motion, are impacted by smoking as well.
“Smoking can actually cause breakdown of the disk because there’s lack of nutrient exchange, specifically where the bone meets the spine disk,” Dr. Navarasala said. “In terms of the disk itself, the presence of nicotine in the blood stream actually can decrease not only the healing but also the regeneration of the cells within the disk.
“Additional mechanisms of action include lack of blood flow to the muscles that surround the spine. These can include muscles on the back of the spine here that can lead to increased pain and discomfort.”
Read Also: What Do Pain Management Doctors Do For Back Pain
The Link Between Smoking And Chronic Pain
Smoking cigarettes regularly ensures a consistent flow of nicotine to your brain. People who smoke inhale about 1-2 milligrams of nicotine per cigarette, equaling up to 20-40 milligrams per pack. Inhaling tobacco also releases tar and carbon monoxide into your lungs, both toxic substances that can affect your overall health in many ways.
Many researchers have found a link between smoking and chronic pain. Because cigarettes and tobacco products are filled with toxic inhalants, smoking creates many health conditions that result in persistent pain. Smoking-related diseases are certainly not limited to back pain, as cigarette ingredients can have many effects on the human body.
The scientific explanation for smoking and chronic pain comes down to your cells. Nicotine and tobacco can deprive your cells of their necessary functions, which weakens their ability to perform throughout your body. Your diminished cells can create chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, degenerative disc disease and oral pain.
Some researchers find that smoking and pain exist in a positive feedback loop. Some people use their chronic pain as a motivator to smoke, while smoking can also cause chronic pain conditions. This deadly cycle traps millions of Americans every day and can cause far more pain in the long run than it solves.
Quitting Smoking: The Best Thing You Can Do For Your Back Pain
While quitting smoking can cause back pain, this increase in pain is temporary and occurs due to the nicotine withdrawal process.
When you smoked, nicotine triggered the release of dopamine in the brain which masked any pre-existing back pain. When you quit, your body may experience heightened sensitivity to pain due to the drop-off of nicotine. This will level out within one month of quitting, once your nicotine withdrawal subsides.
Smoking, on the other hand, can actually cause a number of back conditions and significantly worsen back pain and spinal conditions, including degenerative disc disease, osteoporosis, and fibromyalgia. Smoking also interferes with the bodys ability to heal properly, and for this reason, many surgeons consider smokers ineligible for spinal surgery.
Quitting smoking is the best thing you can do for your back pain. The process can be challenging, but you dont have to do it alone.
There are a number of smoking cessation pharmacotherapies, strategies, nicotine replacement therapies, and treatments designed to make quitting easier for you.
Talking with a trained, specialist GP is a good place to start. You can book a 100% free, bulk-billed telehealth consultation to start your quitting journey today.
Don’t Miss: Can Urinary Tract Infection Cause Back Pain
To Ease Your Back Pain Stop Smoking
Smoking has been associated with a host of negative health consequences. These include everything from degenerative disc disease and low back pain, to a higher risk of complications following surgery.
In a study, researchers at the University of Rochester Medical Center set out to understand the ways in which smoking affected the amount of pain and disability experienced by people who had painful spinal disorders. The study, Smoking cessation related to improved patient-reported pain scores following spinal care, appears in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. It was published online ahead of print in October 2012.
How the Study Was ConductedThe researchers examined data on 5333 patients who had pain related to a spinal disorder. They looked at the patients smoking history, as well as the patients assessment of their pain during the course of their treatment. On average, the researchers followed up with patients after 8 months. Statistical analyses were used to understand the relationship between the participants smoking habits and their health outcomes.
What the Researchers FoundCurrent smokers reported much higher pain than patients who had never smoked. The average improvement in the amount of pain reported by patients during their care differed between people who did not smoke, and people who currently smoked.
Does Smoking Make Back Pain Worse
Smoking can make back pain worse. There are several factors that come into play here.
Smoking and Pain Sensitivity
Smoking is thought to increase pain sensitivity overall because it interferes with the brains ability to regulate pain signals.
The nicotine content in tobacco essentially tricks the body into feeling good. Nicotine triggers the release of dopamine in the brain, which is the chemical responsible for how we feel pleasure.
When your body receives a hit of nicotine, your brain releases dopamine which increases feelings of pleasure and decreases feelings of pain or discomfort.
However, the pain relief that comes from nicotine is short-term. In between cigarettes, any pre-existing back pain returns again, and often comes back stronger.
So, you reach for another cigarette to abate the pain, and the cycle continues.
Smoking can also cause back pain because smoking promotes increased inflammation through the body. When the body experiences high levels of inflammation, pain can occur or worsen.
Smoking and Blood Flow
When you smoke, the chemicals you inhale impair the circulation of blood through your body. This means your bones and tissues dont receieve enough oxygen.
This decrease in blood and oxygen supply to the bones can cause bone weakening and thinning, particularly in the spinal discs which are naturally low in blood supply.
This can cause lower back pain and spinal deterioration.
Smoking and the Spine
Smoking directly impacts the discs within the spine.
Read Also: What Causes Lower Back And Side Pain
How Smoking Interferes With Chronic Pain Management
Researchers say that smoking interferes with chronic pain management and pain treatment by:
- Exacerbation of painful medical conditions smoking is very harmful to the human body and often leads to diseases which cause chronic pain, not to mention that it can build up in the blood vessels and lead to complications.
- Increasing the perception of pain. Studies show that smoking increases the sensitivity to pain and the patient perceive the pain more acutely.
- Interference with painkillers. Smokers require a more quantity of medicines for pain relief. Commonly used medications in this regard are aspirin and narcotics. Large doses of both drugs are required to reduce pain in the persons who smoke.
Smoking And The Perception Of Pain
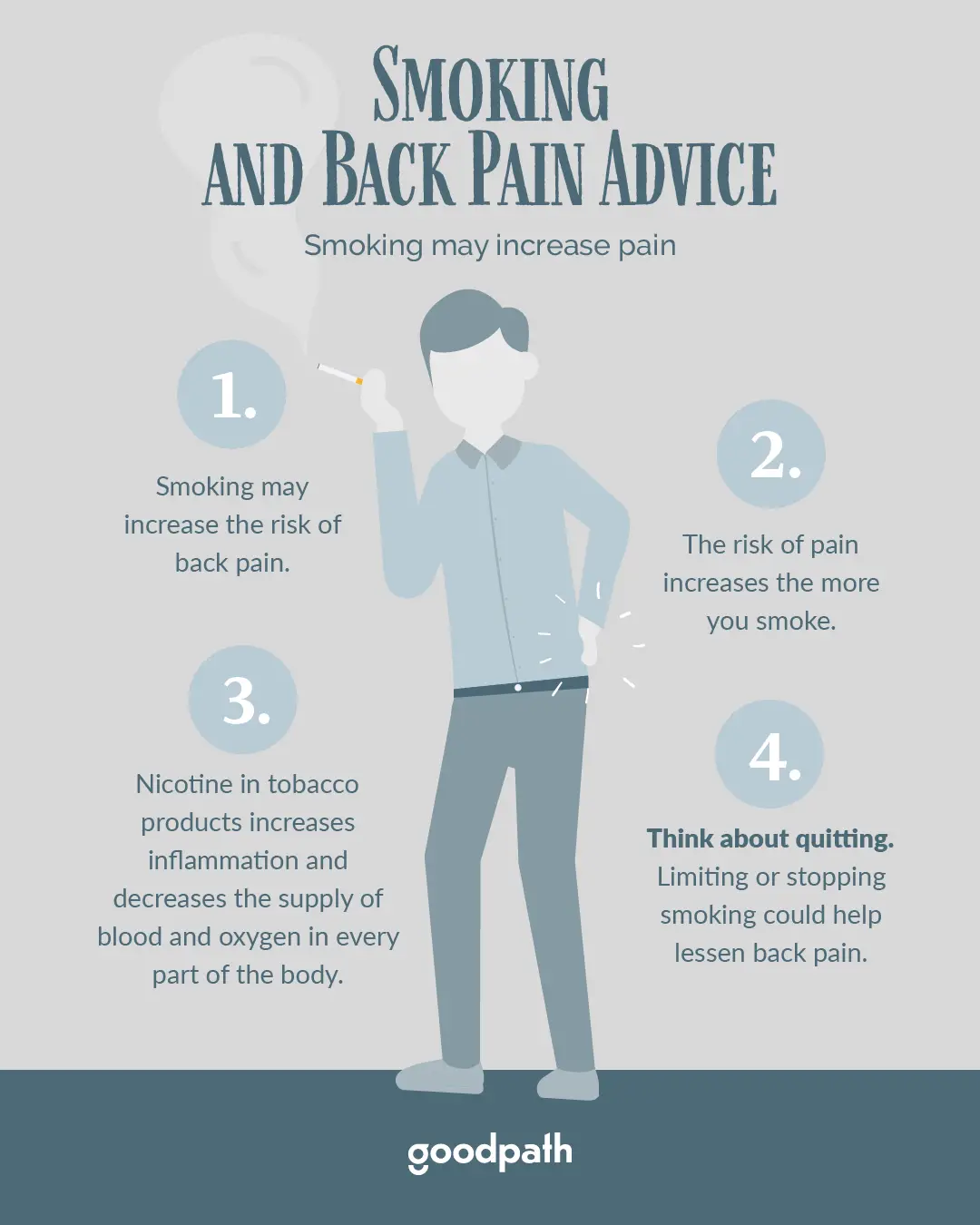
Besides having the potential to cause multiple health problems, smoking also increases pain sensitivity in general. The habit of lighting up is associated with fatigue, which can make existing pain seem more noticeable. Smoking also causes you to tolerate any pain less well.
Smoking cigarettes also affects your brain activity, which can affect how you experience pain. For smokers, symptoms of pain may seem more intense and unrelenting. The good news is that if you quit smoking, many smoking-related health problems improve rather quickly, including this tendency to experience more intense pain.
Recommended Reading: Do Tempurpedic Mattresses Help With Back Pain
Another Good Reason To Quit Smoking In New Year: Less Back Pain
- Another Good Reason to Quit Smoking in New Year: Less Back Pain
A University of Rochester Medical Center analysis of more than 5,300 patients followed for eight months during treatment of spinal disorders showed that cigarette smokers reported far more pain than never-smokers or those who had quit.
Smoking cessation either prior to treatment or during the course of care was related to significant improvements in pain a result that underlines the need for structured stop-smoking programs among the legions of patients who experience back pain due to degenerative disease, deformity, or musculoskeletal problems, said Caleb Behrend, M.D., chief resident in the Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation at URMC.
Glenn R. Rechtine, M.D., a nationally recognized spinal surgeon and adjunct faculty at URMC, led the study, which was published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.
We found that people who stopped smoking had meaningful benefit by reduction of their pain, said Behrend. The pain improvement is in addition to all the other benefits you gain from quitting.
The relationship between pain and smoking is complex and full of contradictions. Nicotine has analgesic properties, for example, and yet clinical evidence shows that smokers are at higher risk for developing back pain and other chronic pain disorders, according to the American Society of Anesthesiologists.
# # #
Quitting Smoking To Combat Neuropathy Pain
Neuropathy Pain
Quitting smoking, even to combat neuropathy pain, is a difficult undertaking. You smoke when you wake up, maybe with your morning coffee. You smoke to relax, smoke after dinner, smoke throughout the day. Simply, you smoke because you enjoy it. Believe me, I understand that quitting smoking is hard.
But quitting smoking is one of the first steps you should take when it comes to tackling neuropathy pain. The next step is finding the right treatment and the right doctor, which Ill touch on shortly.
A few years ago, my patients witnessed me pushing through my days, fighting the burning, and eventually being overtaken by neuropathic pain. I experienced it allthe burning, the ache, the numbness and eventually feeling like a prisoner in my own body. Yes, Ive been where you are now. I worried that I wouldnt be able to continue working in the profession that I love.
Doctors from some of the top medical institutions in the country told me there was little to be done. Eventually, though, being a Harvard graduate, I relied on my own research skills. Soon, I was able to not only halt my neuropathic pain but reverse my neuropathy altogether.
Yes, Ive heard the saying: A doctor who treats himself has a fool for a patient. Ive heard it, but I just dont believe it. How can I believe it? Today, I am healthy, happy, pain-free and able to continue working in a career that I love.
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Lower Back Pain During Pregnancy
Nicotine Weakens Bones Slows Healing
Smoking also increases your risk for osteoporosis, a bone-weakening disease that can cause back pain and increase risk of hip and other bone fractures.
Plus, nicotine can slow healing of bone fractures. Its why patients who need fusion surgery of the spine are asked to stop smoking at least a month before surgery.
In fusion surgery, hardware is implanted in the patient, and the bones have to grow and fuse into the hardware, Dr. Eakins explains. Studies have shown that the failure rate of fusion surgery is twice as great for smokers than nonsmokers due to nicotines stifling effects on bone growth.
Dr. Eakins adds, Studies have found that people who smoke are more likely to have chronic pain, and not just back pain. And there are studies that link smoking to chronic back pain.
A Northwestern Medicine study, for instance, found that smokers are three times more likely than nonsmokers to develop chronic back pain. Quitting smoking cuts the risk of developing the condition.
Can Quitting Smoking Cause Back Pain
Occasionally, people report worsened back pain after quitting smoking. This happens due to the nicotine withdrawal process.
When you smoke, over time, your body becomes dependent on nicotine. Your brain becomes used to receiving a regular dose of nicotine, and when you go without a cigarette for a few hours or more, your body begins to crave another hit of nicotine.
At this point, your body enters a state of nicotine withdrawal. Your body then signals that it desires another cigarette through a range of uncomfortable symptoms including cravings, anxiety, irritability, flu-like symptoms, stomach upset, headaches, and increased sensitivty to pain.
Nicotine withdrawal essentially unmasks any pre-existing pain or conditions that were temporarily relieved by the nicotine-induced dopamine release.
In other words, when you quit smoking, nicotine is no longer tricking your brain into releasing dopamine and interrupting your pain signals, which means youll feel any pain that was already there more intensely.
Nicotine withdrawal is at its most intense in the first three days after quitting. The physical symptoms of withdrawl, including increased pain, will reduce in intensity within the first few days of quitting, and taper off completely within about 4 weeks.
Its important to remember that while quitting can cause a temporary uptick in back pain, this will pass. Back pain caused by smoking, on the other hand, will worsen the longer you continue to smoke.
Also Check: How To Sleep With A Sore Lower Back