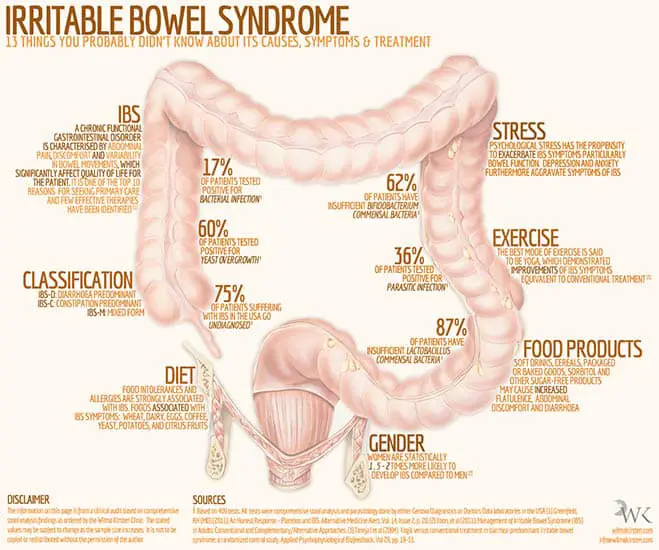
How Does Ibs Affect My Body
In people with IBS, the colon muscle tends to contract more than in people without the condition. These contractions cause cramps and pain. People with IBS also tend to have a lower pain tolerance. Research has also suggested that people with IBS may have excess bacteria in the GI tract, contributing to symptoms.
Easing Bloating And Cramping
IBS can cause bloating or cramps after eating. There are some things you can do which will ease any bloating or cramping you may have. These include:
- eating small but regular meals
- eating oats regularly
- avoiding foods that are hard to digest such as cauliflower and Brussels sprouts
- exercising regularly
Why Would Celiac Patients Have Back Pain
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition. Just as the new study suggests, there may be some autoimmune/inflammatory reactions involved in the creation of low back pain. Perhaps generalized inflammation is at the root of the symptoms. Whatever the mechanism, the studies cited earlier suggests inflammation is at work in the spine of a large majority of patients with celiac disease.
Recommended Reading: Is Motrin Good For Back Pain
Also Check: Does Aleve Help Lower Back Pain
What Are The Causes Of Ibs
Until recently, irritable bowel syndrome was thought to result from altered pain sensitivity and changes in the contractions that move food through the intestines. However, this doesnt account for the range of symptoms experienced by IBS patients.
Scientists are investigating other causes of IBS, including infection, an imbalance in neurotransmitters such as serotonin, overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine, the two-way communication between the gut and the brain, and genetics.
Food sensitivities have also been linked to IBS symptoms. For example, some people with IBS find that chocolate causes constipation or coffee causes bloating. However, its more common for foods high in fermentable carbohydrates such as sucrose and fructose to cause abdominal discomfort.
IBS is a complex interplay between the immune system, central nervous system, and the gut microbiome, and the link between stress and IBS is well known. Studies have shown that psychological stress can increase pain sensitivity, gut contractions, mucus secretion, and gut lining permeability.
Other Features Suggesting That The Pain Is Due To Your Ibs:
According to Rome IV criteria, the IBS Pain is:
- Associated with meals: usually, the IBS pain increases after meals. Especially known food triggers like FODMAPs and gas-producing foods.
- Associated with defecation: some IBS patients report relieve of IBS pain with defecation. Others report worsening of IBS pain during or after defecation.
- IBS pain frequency: the IBS pain is chronic, your first time experiencing IBS pain should be 6 months ago or more. The IBS pain occurs at least once per week.
- IBS pain character: IBS is described as cramps or colics. Usually associated with bloating and gas distension.
- Associated with changes in stool character: Yellow stool , Mucus in stool, and Hard stools .
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Mattress For Back Pain
Prevention Of Abdominal Pain
In many cases, abdominal pain can be prevented by adopting lifestyle and dietary choices that address the cause of your pain. Constipation, digestive upset, and even abdominal injury can often be prevented.
The following steps may help you prevent abdominal pain:
Drink plenty of water.
Develop regular bowel habits. Many people can train themselves to have regular bowel movements to help avoid constipation.
Follow a balanced, fiber-filled diet. Eating a variety of fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods, like whole grains, can help support healthy digestion and reduce constipation.
Eat regularly and slowly. Eating moderately-sized meals, instead of waiting until youre very hungry and stuffing yourself, can help avoid pain from overeating or eating on an empty stomach.
Exercise regularly. Getting enough physical activity can help prevent constipation and strengthen your abdominal muscles, which may help prevent straining.
Wear a seatbelt properly.
Ibs Back Pain Between Shoulder Blades
The pain between the shoulder blades may be due to IBS symptoms. Its also possible for this to be another type of pain, potentially stemming from the gallbladder. The gallbladder is the storage area for bile, a key digestive enzyme whose job it is to break down the fats we consume. This would be another example of referred pain.
Even though the pain between the shoulder blades is a reasonable distance from the gallbladder, this pain may be originating from the gallbladder.
If gallstones are formed in the gallbladder, this impacts bile flow and may even cause a blockage. This can result in symptoms such as
- Pain between the shoulder blades
- Pain in the upper right portion of the stomach
- Pain in the middle of the stomach or below the breastbone
- Since the release of bile is stimulated by the ingestion of fats, these symptoms of pain may worsen following a meal that contains fats. Particularly in the presence of gallstones.
Also Check: Who Can I See For Back Pain
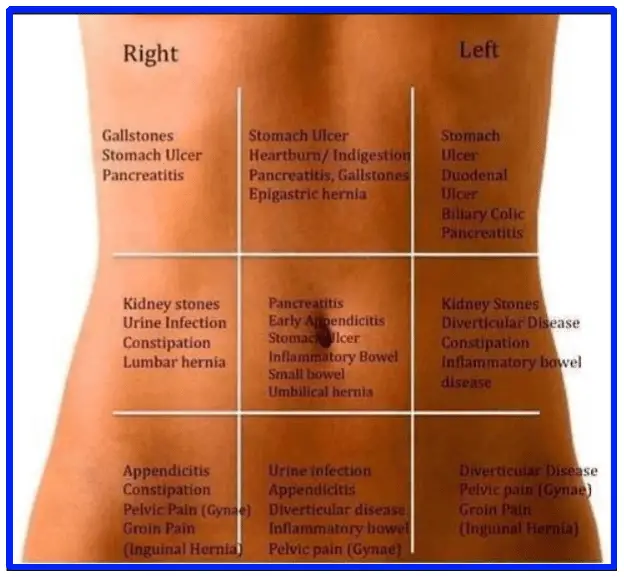
How Ibs Can Cause Back Pain
Most experts agree that IBS back pain is most likely to be a form of referred pain. Referred pain occurs when dysfunction in one area of the body causes discomfort elsewhere.
In the case of IBS, symptoms like constipation, excess gas, and bloating could potentially cause pain in the lower back. However, scientists are still working to find out the precise mechanism behind IBS back pain.
Another theory is that referred pain may be due to dysfunction of a large muscle called the diaphragm. This dome-shaped structure spans the interior torso and plays a crucial role in breathing. Some researchers believe that people with IBS may have abnormal electrical activity within this muscle.
Finally, there is significant overlap between IBS and fibromyalgia. Fibromyalgia causes numerous symptoms, the most common of which is widespread pain. Therefore, anyone suffering from IBS and pain in multiple parts of the body could ask their physician whether fibromyalgia might be the cause.
Back Pain Due To Irritable Bowel Syndrome
A frequent complaint and diagnosis are colon spasms or irritable bowel, a syndrome that occurs more often in women, also during the menstrual cycle. When you suffer from abdominal pain and bloating, it is possible that you suffer from IBS or irritable bowel syndrome. One of the symptoms is a very painful lower back.
Pain in the lower abdomen and the lower back occurs in various ways. Depending on the condition, you can feel the pain in a specific part of the abdomen, for instance at the bottom. Sometimes the entire abdomen can be painful with a painful feeling in the sides and the lower back or in the lower back and the pelvis. This does not always mean it is serious. Many women have this periodically. A hot water bottle and pain killers are still the best cure. In the event of serious pain, you must contact a GP.
You May Like: What Would Cause Lower Back Pain On The Left Side
After The Visit To The Doctor
Do not expect an instant cure or immediate diagnosis. Multiple office visits and tests are often necessary to establish the diagnosis and/or to exclude serious illnesses. Doctors may start you on a medication before a firm diagnosis is made. Your response to that medication sometimes may provide your doctor with valuable clues as to the cause. Therefore, it is important for you to take the medication prescribed.
Notify your doctor if your symptoms worsen, if medications are not working, or if you think you are having side effects. Do not self-medicate without discussing it with your doctor. Even the best physician never bats 1000, so do not hesitate to openly discuss with your doctor referrals for second or third opinions if the diagnosis cannot be firmly established and the pain persists. Self-education is important, but make sure what you read comes from credible sources.
You May Like: Can You Have Heartburn Without The Burn
Tips To Relieve Ibs Back Pain While Sleeping
IBS back pain can make it difficult to get restful sleep. However, with some diligence and a routine, you can be certain you are doing your best to limit the amount of back pain experienced with IBS. Try these tips:
- Exercise everyday
- Avoid large meals and caffeinated drinks at least four hours before bed
- Your bed should not be used for anything else besides sleep and sex.
- Dont sleep or lie down immediately after working out. Instead, try to incorporate a resting period during your exercise time.
- Have a consistent sleep and wake times
Having back pain and IBS symptoms can be a challenge to deal with. If you find yourself losing an excessive amount of sleep or the pain is unbearable, seeing a doctor about your symptoms is recommended. It is possible that your back pain could be due to a different cause, or at the very least, your doctor may prescribe you something to deal with the pain.
Don’t Miss: Does Back Pain Make You Tired
Can Physical Therapy Help Lower Back Pain
Physical therapy is one of the best ways to treat lower back pain, and if your bowel problems are related to back pain, it will ease those symptoms as well. Physical therapy will help ease lower back pain and help you find relief in motion. If you are struggling with this, it is best to seek physical therapy as soon as possible. This will help prevent any need for an operation down the line. In the worst cases, if you do need surgery, our team will be by your side every step of the way helping you recover.
To learn more about lower back pain treatment and our other physical therapy services, call ProFysio Physical Therapy at 812-5200 or contact us online.
Categories
Types Of Management Options To Ease Ibs Back Pain
Irritable bowel syndrome can cause a variety of symptoms. Most of them affect the digestive system, although they can also occur throughout the body. One example is back pain, which is a common issue for people with IBS.
In this article we will discuss everything you need to know about IBS back pain, including its causes, symptoms, and how to manage it effectively.
You May Like: How To Fix Back Pain
An Introduction To Ibs And Back Pain
Back pain is not a symptom that is usually linked to Irritable Bowel Syndrome, but it can occur when the small and large intestines take up a large area: over three quarters of the abdomen.
Abdominal pain in IBS may be felt both at the front of your body or your back. Pain associated with the abdominal organs can often be experienced away from the area affected. This is known as referred pain and is one explanation why the pain of IBS can be felt in your back.
Symptom Patterns Add Up To Ibs
Certain signs and symptoms occur with IBS. Symptom-based criteria for IBS emphasize a positive diagnosis rather than extensive tests to rule out all other diseases. No tests confirm the diagnosis of IBS.
A detailed history, physical examination, and limited diagnostic tests help confirm the IBS diagnosis. More extensive testing is reserved for specific situations.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Sudden Severe Lower Back Pain
The Link Between Ibs And Back Pain
In addition to abdominal-related symptoms, research shows that people with IBS are likely to feel pain in other parts of the body. As many as 81% of people with IBS may also experience back pain.
While the root cause of this back pain varies by person, researchers think it could be linked to IBS in the following ways:
- Physical factors:Sensations in the intestines like gas pressure, colon spasms, or swollen bowels can lead to pain in the abdomen and lower back.
- Referred pain:In many health conditions, pain originating in one part of the body can be felt in another part of the body .
- Another health condition:People with IBS often experience other inflammatory health conditions at the same time, such as fibromyalgia, interstitial cystitis, or rheumatoid arthritis. These conditions can include back pain as a primary symptom.
How Tight Hip Flexors Affect The Reproductive System And Urinary Tract
Just as the digestive system can impact muscle health, the reproductive organs and urinary tract are part of your abdominal health as well. Issues with your kidney, bladder, or reproductive organs can affect body alignment and iliopsoas tightness.
When your body is going through significant change or trauma, this muscle reaction becomes even more elaborate. For instance, when a woman experiences pregnancy and childbirth, there are some major adjustments her body must make. This additional trauma often causes the iliopsoas muscles to overtighten: theyre attempting to stabilize and realign the hips and back.
Other major organ traumas like ovarian cysts can cause issues with the iliopsoas muscles. The ovaries are very close to the iliopsoas muscle, so once theyre inflamed, the muscle contracts and tightens to keep the area safe and protected.
If you are unsure if you have ovary issues, but you are having groin or abdominal pain, it is important to note muscle tightness. Tight iliopsoas muscles alone can cause groin and abdominal pain, so pain may not necessarily be attributed to the organ itself.
Read Also: How To Relieve Lower Back Pain From Sitting
Ibs Chest Pain Symptoms Compared To A Heart Problem
Dr. Lacy explains, Chest pain that is cardiac in origin is often associated with an elevated pulse , shortness of breath, diaphoresis with pain that radiates from the chest into the neck and left arm.
Chest pain that originates from the esophagus or stomach is usually underneath the sternum or in the epigastric region, does not radiate to the neck or left arm, and is unlikely to be associated with diaphoresis or shortness of breath.
Note that both heart attack pain and gastroesophageal reflux disease can cause pain in the back, but irritable bowel syndrome does not.
IBS, which is often associated with spasms of the colon or small intestine, can cause chest pain in some individuals, says Dr. Lacy.
It is easy to understand how a patient with IBS, who has spasms in the colon or small intestine, might also have spasms in another part of the GI tract such as the esophagus.
Recommended Reading: Does Iud Cause Back Pain
What Is Ibs Pain
IBS is a painful condition for many people. In fact, pain is the number one reason people see a doctor for IBS.
While IBS pain can be felt in multiple places around the body, it is most commonly experienced in the lower abdomen .
IBS pain can occur after eating and may be relieved or worsen after a bowel movement. It can range from mild discomfort to a stabbing pain that can be so intense it is sometimes mistaken for appendicitis or heart attack pain.
Pain is a key symptom in assessing whether someone has IBS. The current medical guidelines, also known as the Rome IV criteria, required that for an IBS diagnosis, a person needs to experience: âââ
âRecurrent abdominal pain, on average, at least one day/week the last three months, associated with two or more of the following criteria:
- Related to defecation
- Associated with a change in frequency of stool.
- Associated with a change in form of stool.â
IBS pain that lasts for more than six months is known as chronic pain. Chronic pain with IBS may mean that you feel pain or discomfort consistently or that you are experiencing frequently recurring pain often over an extended period of time.
Although abdominal pain is the most common type of IBS pain, research now indicates that people with IBS are more likely to experience other kinds of pain, including headache, back pain, and muscle ache.â
Also Check: What Does Ibs Mean In Texting
Read Also: Can A Bad Hip Cause Back Pain
Urgent Advice: See Your Gp Urgently If:
You have other symptoms, including:
- a change in your bowel habits that has lasted for more than six weeks, especially if you are over 50 years of age
- unexplained weight loss
- a swelling or lump in your stomach or back passage
- bleeding from your back passage
These can sometimes be a sign of a potentially more serious condition.
You should also tell your GP if you have these symptoms and a family history of bowel cancer or ovarian cancer.
So How Are Ibs And Headaches Connected
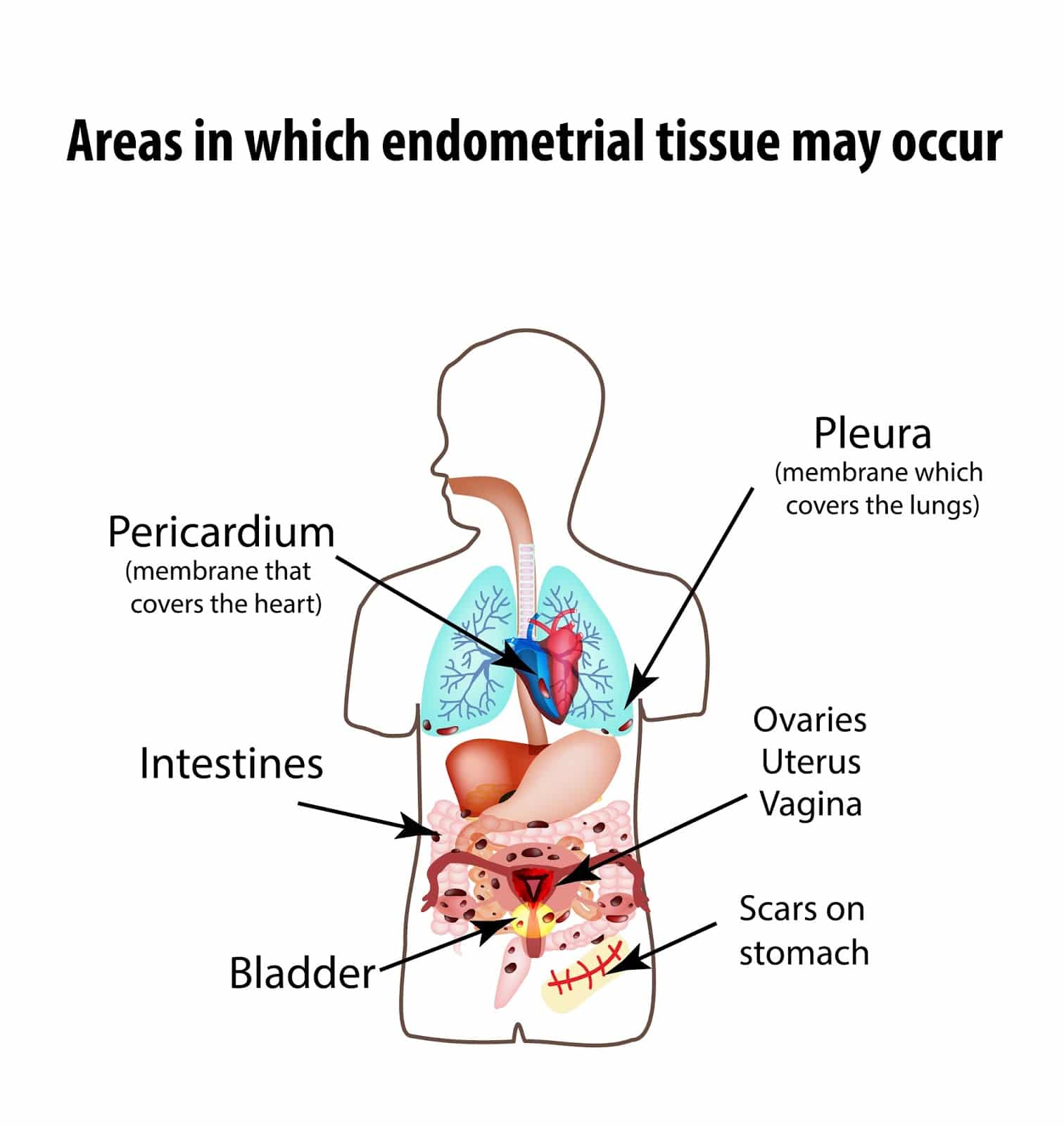
While the exact reason is unknown, one theory is that itâs the result of the relationship between the gastrointestinal system and the central nervous systemâ also known as the gut-brain axis.
The vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve in the body, connects the brain to the gut along the gut-brain axis. This nerve sends communications bi-directionally, meaning it can relay pain signals and information from the brain to the gut and vice versa. Because the vagus nerve is involved in both migraine pain and IBS symptoms, itâs often thought to be implicated in the overlapping symptoms.
Additionally, recent research into the migraine/IBS link has also identified two neuropeptides that may contribute to both migraine symptoms and gastrointestinal functions.
An upside to the gut-brain connection is that it works both ways. So, while itâs unfortunate that what happens in your gut can affect your head, there is evidence that what happens in your mind can also affect what in your gut. This is why treatments like hypnotherapy for IBS may effectively relieve IBS and headache symptoms without the need for drugs or diets. â
Don’t Miss: What Helps Nerve Pain In Lower Back
Can The Chronic Pain State Be Reversed
Chronic pain can be turned around and reversed if done with the proper treatment interventions. This often includes the use of central acting agents, or neuromodulators, and psychological approaches, along with self-management steps that individuals can take on their own. Combining therapies together can be more effective than using just one approach.
While still theoretical, its been shown in practice that even the structural changes involving nerve cells can be reversed. Although chronic severe pain can reduce the number of brain cells, studies using brain imaging have shown that various interventions can result in neurogenesis, the regrowth of nerve cells.
Recommended Reading: How To Help Back Pain From Standing All Day