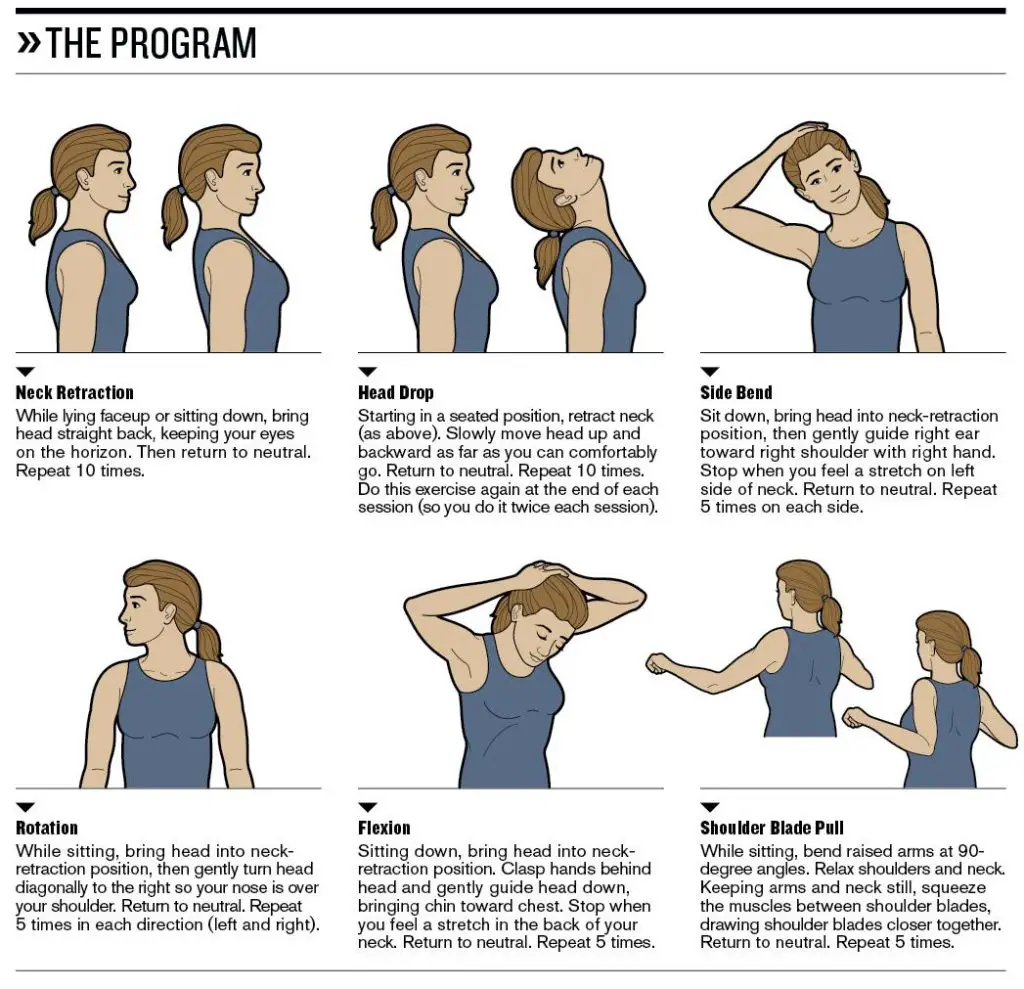
Is It Better To Sit Or Stand With A Stiff Lower Back
A standing desk may help improve your posture and take the stress off your neck and lower back however, it is unlikely to help you correct more severe issues, such as scoliosis or a bulging disc.
These are my observations on standing desks:
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public LiaisonNational Institute of Neurological Disorders and StrokeNational Institutes of HealthBethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
What Causes Lower Back Pain
Many injuries, conditions and diseases can cause lower back pain. They include:
- Strains and sprains: Back strains and sprains are the most common cause of back pain. You can injure muscles, tendons or ligaments by lifting something too heavy or not lifting safely. Some people strain their back by sneezing, coughing, twisting or bending over.
- Fractures: The bones in the spine can break during an accident, like a car crash or a fall. Certain conditions increase the risk of fractures.
- Disk problems: Disks cushion the vertebrae . Disks can bulge from their position in the spine and press on a nerve. They can also tear . With age, disks can get flatter and offer less protection .
- Structural problems: A condition called spinal stenosis happens when the spinal column is too narrow for the spinal cord. Something pinching the spinal cord can cause severe sciatic nerve pain and lower back pain. Scoliosis can lead to pain, stiffness and difficulty moving.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis to cause lower back pain. Ankylosing spondylitis causes lower back pain, inflammation and stiffness in the spine.
- Disease:Spine tumors, infections and several types of cancer can cause back pain. Other conditions can cause back pain, too. These include kidney stones and abdominal aortic aneurysm.
- Spondylolisthesis: This condition causes the vertebrae in the spine to slip out of place. Spondylolisthesis leads to low back pain and often leg pain as well.
Read Also: How To Fix Lower Back Pain From Sitting
Muscle Tightness In Thighs And Hips
Weve talked before about how hamstring stretches can help alleviate back pain. Tight hamstrings are short hamstrings, and these muscles connect to your lower back. Tightness in your hamstrings can affect the curvature of your lower spine, disrupting the precise alignment of your spine with your pelvis.
Hamstrings may be tight as a result of physical activity, injury, or a failure to stretch before and after exercising. Luckily this problem can be easy to manage at home with some targeted stretching. If you need some help getting started, a physical therapist can help guide you through some basic movements.
Which Lifestyle Factors Contribute To Lower Back Pain
There are three major lifestyle factors that may affect your chances of developing lower back pain:
- Multiple studies have established a link between smoking and lower back pain. Smoking raises inflammation inside the body and hinders the body from healing itself.
- Obesity is also associated with several types of chronic pain, including lower back pain. In people with high body mass index , the stress on the spine increases, contributing to even more wear and tear.
- Your level of physical activity can also play a role in your lower back health. While a sedentary lifestyle could increase your risk of developing lower back pain, so can excessive or strenuous physical activity. Check with your doctor if you are unsure about your ideal level of physical activity.
Recommended Reading: How To Relieve Back Pain In Pregnancy
Exercises For Back Stiffness After Sleeping
To improve muscle balance and prevent back stiffness from occurring in future, a combination of exercises is very effective in management of back stiffness after sleeping or any activities of daily living. These include aerobic conditioning, stretching, twisting, strengthening, static and dynamic leg raise, glute stretches, dead lifts, abs and rope crunches, fitness ball wrap, and hyperextension with fitness ball and so forth. Further the exercise of Standing Hip shift has been advised.
Many exercises can be performed to treat the problem of back stiffness. This physical activity relieves tightness and imbalance in lumbar spine, muscles of lower back and hip muscles. Performing these exercises daily helps to keep the back healthy, develop endurance, flexibility and become strong. The American College of Sports Medicine recommends 150 minutes of aerobic conditioning every week, along with stretching and strengthening 2 to 3 days per week. However, before practicing any exercise one should consult a doctor or a physical therapist to know which ones are appropriate to be followed and to what extent they are needed. All the above mentioned exercises need not be performed since they can do more damage than good if overdone.
How Are Back Spasms Evaluated And Diagnosed
After talking to you about your symptoms and getting a list of your medications, your healthcare provider may ask about your entire medical history. Be sure to mention any trauma to your back. Your provider may diagnose your back spasms based on the symptoms you describe.
Which healthcare providers evaluate and diagnose back spasms?
You can see your primary healthcare provider about your back spasms. If needed, they may send you to a specialist.
What questions might a healthcare provider ask to help diagnose back spasms?
- What does the pain feel like?
- Where is the pain located?
- Have you ever loss control of your bowel or bladder?
- How long do the spasms last?
- How often do you have back spasms?
- Do you get any tingling or numbness in your body?
- Do you ever feel weak or uncoordinated when youre having back spasms?
- What medications are you taking?
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get A Herniated Disc In Lower Back
Does Your Back Feel Stiff Well It May Not Actually Be Stiff Study Finds
- Date:
- University of Alberta
- Summary:
- The feeling of stiffness in your back may mean something else is going, warns a new report.
“My back feels so stiff!” We often hear our friends say.
Well, that doesn’t mean your friend’s back is actually stiff, according to a new study at the University of Alberta’s Faculty of Rehabilitation Medicine.
“A conscious experience of feeling stiff does not reflect true biomechanical back stiffness,” explained Greg Kawchuk, professor and back and spine expert in the Department of Physical Therapy. “When we use the same word, stiffness, to describe a feeling and how we measure actual stiffness, we assume these words are describing the same thing. But that is not always the case.”
In the study, Kawchuk and his team asked participants how stiff their backs felt to them. After that, using a customized device, they measured just how stiff the back actually was.
“There was no relation between biomechanical stiffness and the reported feeling of stiffness,” he said. “What people describe as stiffness is something different than the measurement of stiffness.”
Tasha Stanton, lead author and senior research fellow of pain neuroscience at the University of South Australia, said that the feeling of stiffness may be a protective construct that is created by our nervous system.
“It’s our body’s way of protecting ourselves, possibly from strain, further injury or more pain,” she said.
It could mean they feel their movements are slower and more painful.”
People Are Also Reading
In addition, your disc functions somewhat like a ketchup packet. You know, when you squeeze the ketchup packet on one end the ketchup goes to the other end, and if you squeeze too hard. the ketchup flies out the back of the packet as it tears through the seal.
Your disc is weakest at its back/outside portion. So when you sit a lot to drive or at a computer or bend forward with poor mechanics to lift something heavy, the fluid inside the disc can be pushed through some of the layers of the disc, causing the disc to bulge or herniate, which places pressure on the nerves passing through from your spinal cord.
This pressure or inflammation around the nerves creates stiffness and achiness when you sit and try to stand up from sitting because there is more compression on the nerves. And, since the nerves control the muscles, this pressure or inflammation around the nerves causes the muscles to stiffen up. This, in turn makes it difficult to stand up straight when getting from sitting.
As far as getting out of bed in the morning being an issue, what is occurring here is that as you lie down for 6 to 8 hours, fluid builds in the disc a bit and when you go to stand up, there is again less space for the nerves passing through and they are a bit compressed, causing the muscles to stiffen.
So how do you get out of bed in the morning and after sitting without feeling like youve aged beyond your years?
Miller
You May Like: What Should You Do If You Have Lower Back Pain
Three Reasons For Stiffness In Back When Sitting
- Increased pressure on your discs
Arthritis Of The Spine
Arthritis of the spine the slow degeneration of the spinal joints is the most frequent cause of lower back pain. All of us experience wear and tear as we age, and it is normal for your lower back to start acting up as you get older. As the cartilage breaks down between the spinal joints, surrounding tissues may become inflamed. The inflammation and the thinning of cartilage increase friction in the joints, which may cause pain in the lower back.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Waking Up With Back Pain
Meet Tria Neck And Back Strengthening Program: A Leader In Active Physical Therapy Programs
Your active physical therapy program needs to be intensive and specifically designed to strengthen and condition your back and core. And early on, you need specialized equipment that can help you target those specific muscles. Thats where TRIA Neck and Back Strengthening Program can help.
We opened TRIA Neck and Back Strengthening Program nearly 30 years ago, and weve worked with more than 200,000 patients in that time.
Our active physical therapy program for back pain focuses on spine strengthening. Through this program, youll start by doing an intake with a doctor or a physical therapist who specializes in spine care. Theyll work with you to determine your best treatment plan. Then youll start working one-on-one with a physical therapist who specializes in helping people heal chronic pain.
Want to learn more about TRIA Neck and Back Strengthening Program? Watch this short video.
Your therapy will happen at one of our facilities that features state-of-the-art medical exercise equipment. Programs range usually from six to 12 weeks, but it all depends on your progress and your goals. Youll learn about what chronic pain is and how the brain processes it. Youll also focus on body mechanics such as proper lifting, standing and sleeping all the things that can contribute to back pain but you may not think about.
Since our programs are intensive and last for several weeks, its a good time to use your Flexible Savings Account dollars or your insurance .
What About When Ageing Is Painful
There are instances when these changes causes back pain and sciatica, however, and this is often because the discs have thinned in a way that causes a pressure on the nerve roots in the spine. This irritates the nerve and can cause pain along the course of that nerve.
This irritation around a nerve causes what we call an inflammatory response in that area, where lots of irritating chemicals are released around a nerve causing pain .
It is important to note that a disc bulge and degenerative disc disease are NOT the same thing a disc bulge is usually caused by a large tear in a healthy disc, with the bulge directly pressing on the nerve. The pain from a disc bulge is usually more severe than the pain from degenerative disc disease, but disc bulges often improve within 12 weeks while DDD pain may stay at a constant low-moderate level for a long time.
The following video explains the ageing changes that happen to our discs with some handy diagrams:
Recommended Reading: Can Overweight Cause Back Pain
How To Improve Flexibility And Strength
There are lots of simple stretches and exercises you can do to improve flexibility and strength in your lower back.
Focus on lengthening and extending the spine. This helps to relieve compression in the lower back. Stretching the hamstrings is also beneficial.
In addition, you should choose exercises that focus on working the hips, core, and gluteal muscles.
Doing daily activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga is recommended. Put forth dedicated effort into being active as often as possible. Consistently doing exercises and activities to loosen up your lower back will usually yield positive results within a few weeks.
Here are nine exercises you can add to your daily routine to help strengthen your lower back and improve flexibility.
This exercise increases flexibility, relieves tension, and helps to loosen the lower back and hip muscles. You can also engage your core muscles if comfortable.
Muscles used:
How Common Is Lower Back Pain
Around four out of five people have lower back pain at some point in their lives. Its one of the most common reasons people visit healthcare providers.
Some people are more likely to have lower back pain than others. Risk factors for lower back pain include:
- Age: People over 30 have more back pain. Disks wear away with age. As the disks weaken and wear down, pain and stiffness can result.
- Weight: People have overweight/obesity or carry extra weight are more likely to have back pain. Excess weight puts pressure on joints and disks.
- Overall health: Weakened abdominal muscles cant support the spine, which can lead to back strains and sprains. People who smoke, drink alcohol excessively or live a sedentary lifestyle have a higher risk of back pain.
- Occupation and lifestyle: Jobs and activities that require heavy lifting or bending can increase the risk of a back injury.
- Structural problems: Severe back pain can result from conditions, such as scoliosis, that change spine alignment.
- Disease: People who have a family history of osteoarthritis, certain types of cancer and other disease have a higher risk of low back pain.
- Mental health: Back pain can result from depression and anxiety.
Don’t Miss: What Does Lower Back Pain On The Right Side Mean
What Are Back Spasms
A spasm is when your muscles suddenly and against your will. They may painfully twinge, seize or contract. The muscles in your upper, middle and lower back are divided into three types: intrinsic/deep muscles, superficial muscles and intermediate muscles. Lower back spasms are more common, but any muscle can contract.
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis is calcification or a bony hardening of ligaments in areas where they attach to the spine. Ligaments are supposed to be flexible, so DISH can cause symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and restricted movement.
You should visit your primary care physician who will be able to confirm the diagnosis with X-ray, and localize the problem to specific areas in your spine. This disease is managed with pain medication, physiotherapy, and, in rare cases, surgery.
Rarity: Rare
Top Symptoms: joint pain, upper back pain, stiff neck, stiff back, trouble swallowing
Urgency: Primary care doctor
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Lower Back Feel Stiff