Lower Right Back Pain From Internal Organs
There are numerous possible sources of lower right back pain in the organs of the mid-back, abdominal, or pelvic regions. Pain may start following inflammation or irritation of an internal organ, or may be a sign of infection. These conditions will usually produce other symptoms with lower right back pain that more specifically narrow down the source.
Several common internal causes of lower right back pain include:
When To Call A Doctor
Consult your doctor if you have back pain thats intense, worrisome, or that doesnt go away with self-care measures. Its also important to call your doctor if your lower back pain is making it hard for you to go about your daily activities.
Most cases of lower back pain on the right side are not medical emergencies. However, dont hesitate to get immediate medical help if you experience back pain thats accompanied by any of the following symptoms:
- loss of bladder or bowel function
- sudden, severe pain
- weakness or loss of sensation in your lower body
- pain accompanied by fever, clammy skin, a rapid heart rate, nausea, vomiting, or any other concerning symptoms
The appropriate treatment for lower back pain emergencies depends on the cause. If the source of the pain isnt obvious, you may need one or more of the following screenings to determine the right course of action:
- an MRI to check your spinal cord, nerve roots, and other soft tissue
- an X-ray to look at your spine and other joints for signs of fracture or other concerns
- blood tests to check for markers of inflammation
If nerve or muscle problems are the cause of lower back on the right, epidural injections of corticosteroids may be necessary if the pain and loss of mobility and function are severe.
If appendicitis is diagnosed and it cant be managed by antibiotics, then emergency surgery to remove the appendix may be necessary.
- nerve compression in your spine
- disc degeneration
- an abdominal aortic aneurysm
- appendicitis
What Are The Symptoms Of Lower Back Pain
Symptoms of lower back pain can come on suddenly or appear gradually. Sometimes, pain occurs after a specific event, such as bending to pick something up. Other times, you may not know what caused the pain.
Pain may be sharp or dull and achy, and it may radiate to your bottom or down the back of your legs . If you strain your back during an activity, you may hear a pop when it happened. Pain is often worse in certain positions and gets better when you lie down.
Other symptoms of lower back pain include:
- Stiffness: It may be tough to move or straighten your back. Getting up from a seated position may take a while, and you might feel like you need to walk or stretch to loosen up. You may notice decreased range of motion.
- Posture problems: Many people with back pain find it hard to stand up straight. You may stand crooked or bent, with your torso off to the side rather than aligned with your spine. Your lower back may look flat instead of curved.
- Muscle spasms: After a strain, muscles in the lower back can spasm or contract uncontrollably. Muscle spasms can cause extreme pain and make it difficult or impossible to stand, walk or move.
Recommended Reading: Back Pain Cleveland Clinic
Lower Back Pain Causes: 8 Reasons For Sudden & Chronic Pain
Sometimes, you know exactly why your back is hurting. Maybe you lifted something awkwardly and felt the pain right away. Or maybe your doctor has been warning you for years that your bad posture would lead to lower back pain.
But other times, the source of back pain can feel like a mystery.
“Your lumbar spine, located in your lower back, plays a crucial role in supporting the weight of your upper body. It’s also responsible for everyday movements, such as bending, twisting and coordinating the muscles in your hips, pelvis legs and feet,” says Dr. Kenneth Palmer, orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at Houston Methodist. “Due to heavy use, the bones, muscles, ligaments, disks and nerves found in your lumbar spine are quite susceptible to both injury and wear and tear over time causing pain in the lower back.”
Lower back pain symptoms include:
- Dull ache in your hips and/or pelvis
- Muscle spasms or tightness
- Sharp, tingling pain that starts in your lower back and travels down one leg
- Pain that worsens with sitting and quickly improves while walking
- Pain that is noticeably worse in the morning
“Typically, a person experiences some combination of these symptoms, which can develop suddenly or over time. In some cases, lower back pain can feel like it comes and goes flaring up now and then, but generally getting progressively worse over time,” explains Dr. Palmer.
Speaking of the various causes of lower back pain…
Muscle Imbalances And Trigger Points
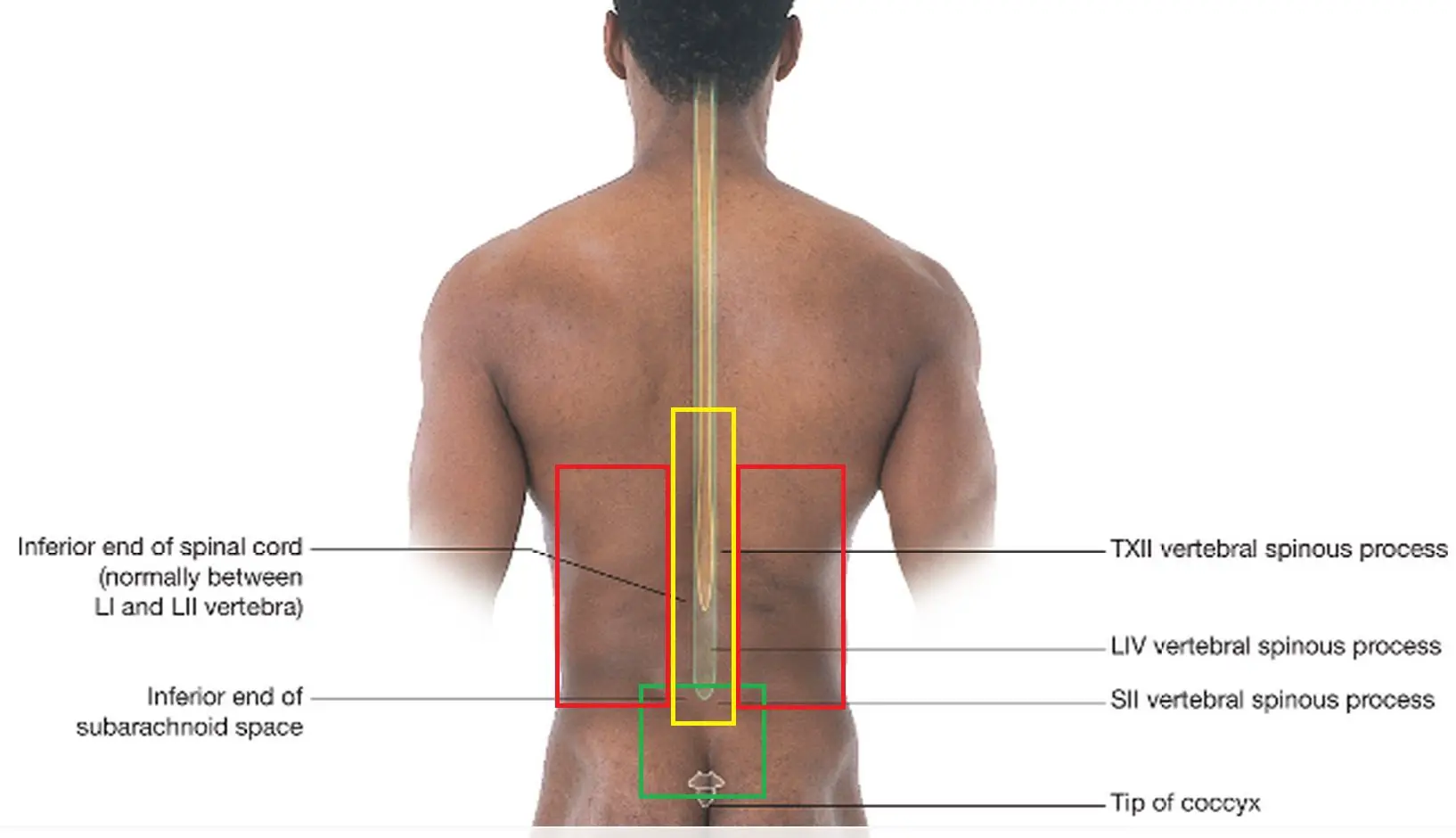
To help you sit, stand, walk, run and otherwise be active, the muscles, bones, and joints of the body have an uncanny way of “robbing from Peter to pay Paul,” so to speak. It’s all in the name of keeping you balanced and moving.
But for whatever reason the balance that’s established is often not the most ideal, leading to some muscles getting very tight, and others becoming overstretched and taut. In this case, you may develop painful spasms or trigger points on one side of the body or the other.
Muscles commonly affected include your quadratus lumborum which is your flank muscle and your gluteus medius which is located at the side of your hip, and plays a key role in keeping you from excessive side to side movement. Both can lead to pain on the right side of your back, depending on the nature of the imbalance.
Don’t Miss: Exercise For Lower Back Pain Mayo Clinic
All The Red Flags For Ominous Causes Of Back Pain
Red flags are signs or symptoms that something medically ominous may be going on. Red flags are not reliable, and their presence is not a diagnosis. When you have some red flags, it only indicates a need to look more closely. Sometimes red flags are missing even when there really is something serious going on and sometimes they are a false alarm.24 Check off all that apply hopefully none or few or only the least alarming of them!
Some of these red flags are much less red than others, especially depending on the circumstances. For instance, weight loss is common and often the sign of successful diet! Obviously, if you know of a harmless reason why you have a red flag symptom, it isnt really a red flag . But every single actual red flag in combination with severe low back pain thats been going on for several weeks is definitely a good reason to get yourself checked out.
Most people who check off an item or two will turn out not to have an ominous cause for their low back pain. But why not check?
What Are Some Common Lower Back Pain Causes
The causes of lower back pain are sometimes viewed as being mechanical, organic or idiopathic. Sometimes spinal conditions are congenital or acquired meaning the disorder develops later in life.
- Mechanical lower back pain is often triggered by spinal movement and involves spinal structures, such as the facet joints, intervertebral discs, vertebral bodies , ligaments, muscles or soft tissues.
- Organic lower back pain is attributed to disease, such as spinal cancer.
- Idiopathic refers to an unknown cause.
These are some of the things your doctor might look for or rule out when you schedule a visit for back pain.
The common symptoms of lower back pain.
Sprains and strains. Ligament sprains and muscle or tendon strains are the most common causes of lower back pain. Theyre often related to overuse.
Degenerative disc disease. While the name sounds worrisome, it just means you have a damaged disc causing pain. Over time, discs become thinner and flatter due to wear and tear. That leaves them less able to cushion the vertebrae and more likely to tear .
Herniated disc. The protective covering on intervertebral discs can tear over time. When this happens, the soft inner disc tissue may push through the outer layer. A disc that bulges or slips out of place is known as a herniated disc, bulging disc, or slipped disc. The herniation may press on nerve roots, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, numbness or weakness in the area that the nerve serves
Also Check: Tylenol Or Aleve For Back Pain
Is It A Mechanical Problem
In many cases, the pain happens when parts of the back â the spine, joints, tissues, muscles, and the discs that cushion the spinal bones â are out of sync. If your back isnât feeling quite right, have your doctor check for:
Herniated or slipped discs: The bones of your spine are cushioned by discs, often referred to as âshock absorbers.â When they wear down, the soft tissue between them begins to squeeze out. This is when you start to feel it â especially if they rupture. It can happen if youâve had a sudden injury, or because of simple wear and tear.
Bulging discs: The stuff inside your discs âbulges,â but not as much as with a herniated disc. They often cause no symptoms on their own, but they can bring pain if the disc pushes up against a nerve root.
Degenerative disc disease: The discs that separate your vertebrae wear down. This sometimes causes the bones to rub together. Age is usually the reason, but sports and injuries can be culprits, too.
Inflammation and movement problems of the sacroiliac joint: This joint sits at the bottom of the spine, on either side of the pelvis. It transfers the weight of your upper body to your lower body. This can start to bother you after youâve been injured, if you have an infection, if you have arthritis, or if youâre pregnant. Abnormal movement, such as too much movement of the joint, can also cause long-term pain.
Osteoarthritis: This is when your cartilage and bone begin to break down and there is inflammation.
Lower Back Pain From Appendicitis
Appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed from blockage or an infection. While appendicitis typically causes intense pain on the right side of the abdomen, the pain can still extend to the right side of the back. Common symptoms of appendicitis to look out for include bloating or excess gas, swelling in the abdomen, a loss of appetite, vomiting, nausea, and constipation or diarrhea. Patients should seek out medical care immediately because this serious condition requires the surgical removal of the appendix, referred to as an appendectomy.
Read Also: Advil Or Tylenol For Back Pain
Warm Or Cold Compress
Applying a cold or warm compress to the painful area on the right side of your back can help to relieve inflammation, muscles strains, or nerve pain.
According to researchers from Johns Hopkins Medical Center, heat or cold can help to relieve the symptoms of middle or upper back pain. The advantages of this are as follows:16
- Cold treatment for back pain helps to reduce swelling and restricts blood circulation to prevent bruising or bleeding. This is effective in the first 48 hours after an injury or muscle strain.
- Heat treatment for middle back pain increase circulation to speed up healing and reduces stiffness in joints to relieve rib pain. Use only when swelling and inflammation have gone from the initial injury .
How to make a cold compress for relieving injuries to your ribs:
After 48 hours, you should use a warm compress for pain relief.
How to make a warm compress to relieve back pain under your ribs:
How Is Back Pain Treated
Acute back pain usually gets better on its own. Acute back pain is usually treated with:
- Medications designed to relieve pain and/or inflammation
- analgesics such as acetaminophen and aspirin
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen and naproxen may be sold over the counter some NSAIDS are prescribed by a physician
- muscle relaxants are prescription drugs that are used on a short-term basis to relax tight muscles
- topical pain relief such as creams, gels, patches, or sprays applied to the skin stimulate the nerves in the skin to provide feelings of warmth or cold in order to dull the sensation of pain. Common topical medications include capsaicin and lidocaine.
Exercising, bed rest, and surgery are typically not recommended for acute back pain.Chronic back pain is most often treated with a stepped care approach, moving from simple low-cost treatments to more aggressive approaches. Specific treatments may depend on the identified cause of the back pain.
Read Also: Will Naproxen Help Back Pain
What Causes Low Back Pain
It might develop suddenly, like after you lift something heavy. Or it might come on slowly.
As you get older, the structure of your back begins to show wear and tear. Doctors call it âspondylosis,â which means your spineâs joints, disks, and vertebrae get worse over time. This slow decline can lead to many problems, like the following:
- Strains. This means you overstretch or tear your tendons or muscle. You can do this by twisting, lifting something thatâs too heavy, or lifting something the wrong way.
- Degenerated disks. When these are healthy, they cushion your back as you bend, flex, and twist. As disks begin to wear out, they no longer absorb the shock of these movements well.
- Herniated or ruptured disks. Normal disks are rubbery. When they become squeezed, a portion bulges out between your vertebrae.
- Radiculopathy. A spinal nerve can become pinched or inflamed. This can cause low back pain to travel down your legs. It can also cause numbness or tingling.
- Sciatica. This is the type of radiculopathy that affects the sciatic nerve, which runs from your butt down the backs of your legs. When itâs inflamed, you may feel burning or pain like an electrical shock that may go all the way down to your feet.
- Spondylolisthesis. In this condition, a vertebra slips out of place and pinches spinal nerves.
- Spinal stenosis. Your spinal column may narrow over time, putting pressure on your nerves. Your legs may feel numb and grow weaker.
A Guide To Lower Right Back Pain
In some cases, low back pain is felt entirely or primarily on the right side rather than spread evenly across the back. Understanding the possible causes of lower right back pain, as well as its typical characteristics, can help lead to an accurate diagnosis and more effective treatment.
Lower back pain caused by damage to the soft tissues is extremely common, and most cases will not require urgent care. SeeLower Back Strain Video
You May Like: Advil Vs Ibuprofen For Back Pain
Facet Joint Pain And Spinal Arthritis
Facet joints are interconnecting joints located at the back of the spine collectively, they give the spine its integrity by limiting excessive movement. Each spinal level has a right and left facet joint. Facet joints are also known as zygapophysial joints.
Facet joints are often the site where bone spurs and other arthritic changes occur. Such changes tend to be related to wear and tear, and at any given level, may occur on one facet joint, but not the others. So when they develop on the right side, they may cause right side back pain.
Other symptoms include numbness, tingling, electrical sensations and/or weakness that travel down one extremity.
Lower Right Back Pain From Female
In a similar manner to men, women may exhibit pain in the lower right back from conditions that only affect females. Affecting 1 in 10 females in the United States, Endometriosis occurs when uterine tissue grows outside the womb, often located on the ovaries and fallopian tubes. When the tissue grows on the right ovary or fallopian tube, it can aggravate the organ and surrounding tissue, thereby culminating in pain from the front or right side of the body to the back. Female patients have effective treatments available such as hormonal therapy or laparoscopic surgery. Low-dose birth control bills can help these growths shrink while surgery can extract the growths.
You May Like: Does Aleve Help With Back Pain
You’re Having Problems With Your Bowels Or Urination
If your back pain is paired with a loss of control over your bowels or urination, then it’s time to seek help immediately at a local emergency room. These symptoms point to cauda equina syndrome, where the nerves in the lower spine have become paralyzed. While rare, this syndrome can be permanently damaging to the nerves if left untreated. If you experience these symptoms, especially accompanied by numbness in the legs, then you may need surgery to decompress the nerves and preserve their overall function.
Why Is Lower Back Pain Such A Common Problem
The bottom part of your back typically has just five vertebrae fewer than your neck and mid-back. And these vertebrae do a lot of heavy lifting! Your lower back is where your spine connects to your pelvis, bearing the weight of your upper body. This area experiences a lot of movement and stress, which may lead to wear, tear and injuries.
Don’t Miss: Does Aleve Work For Back Pain