Or You Could Be Dying What Are The Odds That Back Pain Is Something Scary
Of course there are cases of low back pain that have alarming causes, but its reassuringly rare. Once in a while back pain is a warning sign of cancer, autoimmune disease, infection, or a handful of other scary culprits. Over the age of 55, about one in twenty cases turns out to be a fracture, and one in a hundred is more ominous. The further you are from 55, the better your odds.
But how can you tell? It can be tricky. This is a concise, readable guide to symptoms that need better-safe-than-sorry investigation with your doctor. In other words, this article explains the difference between dangerous and just painful as clearly as possible. Tables, checklists, and examples ahead.
What Causes Back Pain
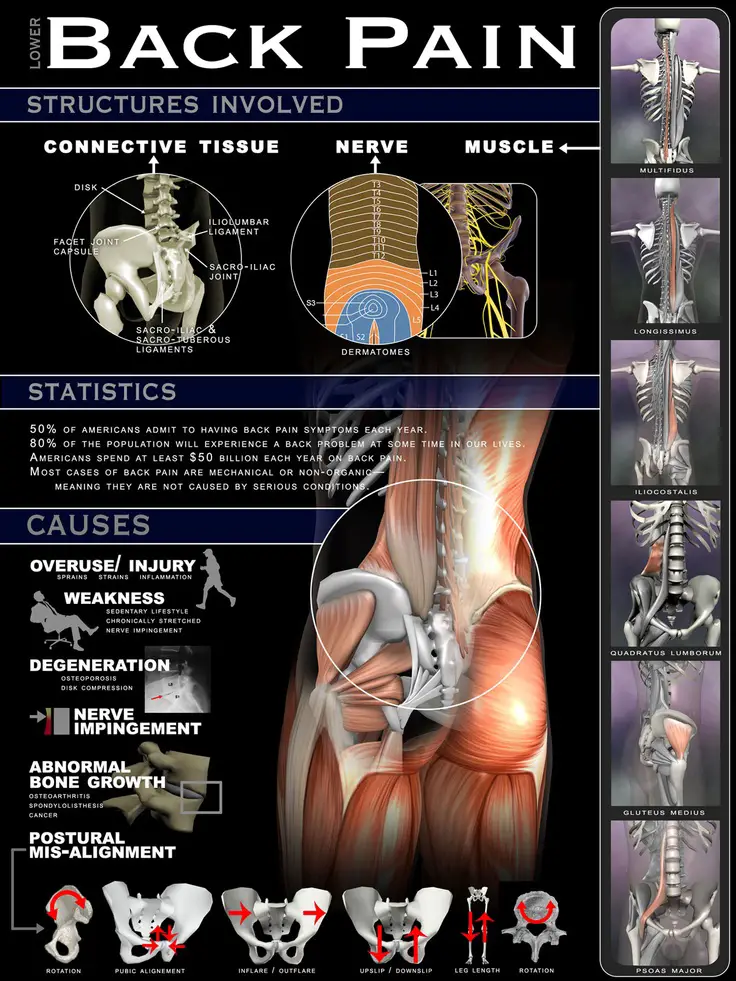
Your spine or backbone is a complex structure that is made up of 24 small bones called vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other. Discs sit between each vertebra to act as cushions or shock absorbers and give your spine flexibility. Vertebrae are joined together by small joints called facet joints. These joints allow you to move and bend your back. A mesh of ligaments and muscles hold the spine together and provide structural support, which allows you to move.
Back pain can originate from any of these structures, but in most cases, this pain doesnt result from any significant damage to your spine. This pain usually stems from surrounding muscles, ligaments or joints and occasionally spinal disc problems.
For at least 9 in 10 people, back pain is not caused by any particular condition and is referred to as non-specific back pain.
This type of back pain results from a range of different factors such as:
- poor posture
- an unhealthy weight
Less than 1 in 100 people have back pain that is related to a serious medical problem such as cancer, infection, a spinal fracture or specific conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis. Research has also shown that you actually dont need to know the cause of back pain to treat it successfully.
Range Of Lower Back Pain Symptoms
Low back pain can incorporate a wide variety of symptoms. It can be mild and merely annoying or it can be severe and debilitating. Low back pain may start suddenly, or it could start slowlypossibly coming and goingand gradually get worse over time.
Depending on the underlying cause of the pain, symptoms can be experienced in a variety of ways. For example:
- Pain that is dull or achy, contained to the low back
- Stinging, burning pain that moves from the low back to the backs of the thighs, sometimes into the lower legs or feet can include numbness or tingling
- Muscle spasms and tightness in the low back, pelvis, and hips
- Pain that worsens after prolonged sitting or standing
- Difficulty standing up straight, walking, or going from standing to sitting
In addition, symptoms of lower back pain are usually described by type of onset and duration:
Don’t Miss: What Causes Pain In Your Upper Back And Chest
Symptoms Of Lower Back Pain
Sometimes a pain may develop immediately after you lift something heavy, or after an awkward twisting movement. Sometimes it can develop for no apparent reason. Some people just wake up one day with low back pain.
Although nonspecific back pain is sometimes called simple back pain, simple does not mean that the pain is mild. The severity of the pain can range from mild to severe. Typically, the pain is in one area of the lower back but sometimes it spreads to one or both buttocks or thighs. The pain is usually eased by lying down flat. It is often made worse if you move your back, cough, or sneeze. So, nonspecific low back pain is mechanical in the sense that it varies with posture or activity.
Most people with a bout of nonspecific low back pain improve quickly, usually within a week or so, sometimes a bit longer. However, once the pain has eased or gone it is common to have further bouts of pain from time to time in the future. Also, it is common to have minor pains on and off for quite some time after an initial bad bout of pain. In a small number of cases the pain persists for several months or longer. This is called chronic back pain .
Sciatica Is Nerve Pain
There are a series of nerve roots that exit from your lower spine. When any of these nerve roots on either side of your lower spine becomes irritated or pinched, pain may radiate from the nerve root to the sciatic nerve. The pain may travel down the sciatic nerve through the buttock and down the back of the leg and into your foot and/or toes. It typically occurs only on one side of the body.
See Types of Sciatic Nerve Pain
The pain is unique often described as a shooting, searing pain that is felt deep in the buttock and radiates down the back of the leg. Numbness, tingling, or burning may also be felt along the nerve. Some people describe the nerve pain as electric-like. Conversely, sciatica symptoms may be experienced as more of a constant, dull pain.
Medical terms used for sciatica include lumbar radicular pain and lumbar radiculopathy.
Many people refer to any type of leg pain as sciatica, but in fact, there are many causes of leg pain that are not medically classified as sciatica and need to be treated differently.
Examples of problems that are not sciatica but can cause similar symptoms include:
- Joint problems in the spine. Pain may be referred from the spinal joints down into the leg. This problem is technically not sciatica, and the treatment for it is different. For example, joint degeneration from spinal arthritis may cause pain that has sciatica-type symptoms.
See When Sciatica Pain Is a Medical Emergency
Don’t Miss: How To Use Exercise Ball For Back Pain
What Exactly Is The Lower Back Anyway
Your lower back is known as the lumbar region of the spine. It has a lot of heavy lifting to do: The lumbar spine carries the weight of your entire upper body, plus biomechanical stresses that occur with movement.
The lumbar spine has five vertebraebackbones. Each vertebra has a large disc cushiony gel wrapped in a tough membrane on its front side that acts as a shock absorber. Each vertebra also has two cartilage-lined facet joints on its back side. Working together, discs and facet joints allow the spine to safely bend and twist.
Your lower back also includes ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Ligaments are strong bands that hold the vertebrae and discs together. Tendons attach muscles to the vertebrae. These structures help limit excessive movement that could harm the spinal cord.
Can Back Pain Lead To Complications
The good news is that most people recover from back pain within a few weeks.1 See your doctor if you experience additional symptoms, such as:
- loss of bowel and/or bladder control
- severe pain that gets worse instead of better over time
- problems with passing urine or bowel movements
- numbness or a pins-and-needles sensation in your legs, back or elsewhere
- unexplained weight loss
- back redness or swelling
For some people, back pain becomes an ongoing problem. Around 1 in every 2 people who experience back pain will experience it again, and for 1 in 5 people, back pain may last beyond 8 to 12 weeks. Possible complications that result from persistent, long-term back pain include:
- dependence on strong pain medicines, such as opioids
- reduced quality of life
- more difficulty finding work and keeping active
See your healthcare professional if your back pain is unresolved and limits your movement and activities. A health care professional can help you find ways to manage your pain and regain a better quality of life.
Read Also: Is Tempurpedic Good For Back Pain
When To See A Doctor
Even though it’s common, most cases of back pain tend to clear up without the need to see a doctor.
You should see your doctor if your pain:
- is really bad
- lasts for a long time
- stops you from working or doing the things you enjoy
- affects your everyday activities
- gets worse.
You should also see your doctor if you have any changes in sexual function, for example, being unable to get an erection.
If the pain is causing you significant problems and stops you from getting on with normal life and work activities, your doctor will examine you and ask you questions.
These questions will help predict how likely it is that you need further help with your back pain. If you do need further support, your doctor will make a referral to physiotherapy so that you can have treatment early, to help with the pain and return to normal activities.
Its natural to want to know what has caused your back pain. However, specialists may not be able to tell you for certain what has caused your back pain, even after carefully assessing you.
If youre concerned about the cause of your back pain, it can help to talk openly about any worries with a healthcare professional, as reducing any fear may help speed up your recovery.
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Lower Back Pain
The diagnosis of low back pain involves a review of the history of the illness and underlying medical conditions as well as a physical examination. A complete story of the back pain must be reviewed including injury history, aggravating and alleviating conditions, associated pain symptoms , as well as the duration and progression of symptoms. Aside from routine abdomen and extremity evaluations, rectal and pelvic examinations may eventually be required as well. Further tests for diagnosis of low back pain can be required including blood and urine tests, plain film X-ray tests, CAT scanning, MRI scanning, bone scanning, and tests of the nerves such as electromyograms and nerve conduction velocities .
Don’t Miss: How Can I Relieve Back Pain During Pregnancy
What Causes Lower Back Pain In Women
Lower back pain doesnt have one specific cause. There is more to this problem than strains and sprains or pregnancy. As mentioned above, some people dont even know what causes pain in this area, but finding out is crucial in order to improve the quality of life and alleviate discomfort you experience.
*All individuals are unique. Your results can and will vary.
Since lower back pain in women has a wide array of different causes and some of them arent even related to your back, well assess the most common factors separately below.
Complementary And Alternative Techniques Include:
- Acupuncture is moderately effective for chronic low back pain. It involves inserting thin needles into precise points throughout the body and stimulating them , which may cause the body to release naturally occurring painkilling chemicals such as endorphins, serotonin, and acetylcholine.
- Behavioral approaches include:
- Biofeedback involves attaching electrodes to the skin and using an electromyography machine that allows people to become aware of and control their breathing, muscle tension, heart rate, and skin temperature people regulate their response to pain by using relaxation techniques
- Cognitive therapy involves using relaxation and coping techniques to ease back pain
Spinal injections include:Trigger point injections can relax knotted muscles that may contribute to back pain. An injection or series of injections of a local anesthetic and often a corticosteroid drug into the trigger point can lessen or relieve pain.
Recommended Reading: Can Liver Cancer Cause Back Pain
What Is Lower Back Pain
Low back pain can result from many different injuries, conditions or diseases most often, an injury to muscles or tendons in the back.
Pain can range from mild to severe. In some cases, pain can make it difficult or impossible to walk, sleep, work or do everyday activities.
Usually, lower back pain gets better with rest, pain relievers and physical therapy . Cortisone injections and hands-on treatments can relieve pain and help the healing process. Some back injuries and conditions require surgical repair.
Can Further Bouts Of Back Pain Be Prevented
Evidence suggests that the best way to prevent bouts of low back pain is simply to keep active and to exercise regularly. This means general fitness exercise such as walking, running, swimming, etc. There is no firm evidence to say that any particular back strengthening exercises are more useful to prevent back pain than simply keeping fit and active. It is also sensible to be back-aware. For example, do not lift objects when you are in an awkward twisting posture.
Read Also: Can A Poor Mattress Cause Back Pain
What Causes Lumbar Strain
Injury can damage the tendons and muscles in the lower back. Pushing and pulling sports, such as weight lifting or football, can lead to a lumbar strain. In addition, sports that require sudden twisting of the lower back, such as in tennis, basketball, baseball, and golf, can lead to this injury.
Certain risk factors can increase the risk for this injury. The risk factors are:
- Severe lower back curvature
- Weak back or belly muscles
- Tight hamstrings
Key Points About Low Back Pain
- Specific treatment for low back pain depends on the cause of the pain and the severity. But it often includes pain medicines and muscle relaxers, physical therapy, and assistive devices such as a back support. It also may include lifestyle changes such as stress reduction, weight loss, and increased physical activity.
- A back rehab program may be used as part of the treatment for low back pain.
- Measures to prevent back pain include using safe lifting techniques, maintaining correct posture, staying at a healthy weight, not smoking, and reducing stress.
Also Check: How To Wear A Back Brace For Lower Back Pain
Prevention Of Lower Back Pain
Looking after your back can help to reduce your risk of getting back pain. It can help to do the following.
- Get plenty of exercise. Keeping active with regular exercise can help to prevent back pain coming back, or reduce your risk of getting it in the first place.
- Take care with lifting and carrying heavy items. Dont lift or carry more than you can manage, and make sure youre using the right technique. This means slightly bending your back, knees and hips when lifting, rather than stooping from your back.
- Keep a good posture. If you work at a desk, make sure your chair, desk and computer screen are set up correctly. Your employer should be able to assess your workstation.
- Move regularly dont sit in the same position for long periods of time.
What Structures Make Up The Back
The lower backwhere most back pain occursincludes the five vertebrae in the lumbar region, which supports much of the weight of the upper body. The spaces between the vertebrae are maintained by round, rubbery pads called intervertebral discs that act like shock absorbers throughout the spinal column to cushion the bones as the body moves. Bands of tissue known as ligaments hold the vertebrae in place, and tendons attach the muscles to the spinal column. Thirty-one pairs of nerves are rooted to the spinal cord and they control body movements and transmit signals from the body to the brain.
Other regions of vertebrate are cervical , thoracic , and sacral and coccygeal segments.
Recommended Reading: How To Cure Chronic Lower Back Pain
Conditions Of Bone And Joint Causes Lower Back Pain
Bone and joint conditions: Bone and joint conditions that lead to low back pain include those existing from birth , those that result from wear and tear or injury, and those that are due to inflammation of the joints .
Congenital bone conditions: Congenital causes of low back pain include scoliosis and spina bifida. Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine that can be caused when one lower extremity is shorter than the other or because of an abnormal architecture of the spine . Children who are significantly affected by structural scoliosis may require treatment with bracing and/or surgery to the spine. Adults infrequently are treated surgically but often benefit from support bracing. Spina bifida is a birth defect in the bony vertebral arch over the spinal canal, often with the absence of the spinous process. This birth defect most commonly affects the lowest lumbar vertebra and the top of the sacrum. Occasionally, there are abnormal tufts of hair on the skin of the involved area. Spina bifida can be a minor bony abnormality without symptoms. However, the condition can also be accompanied by serious nervous abnormalities of the lower extremities.
Chronic Low Back Pain Of No Specific Origin
Low back pain is defined as pain, tightness, and stiffness between the lower end of the rib cage and the buttocks. “Chronic” means the pain has lasted for twelve weeks or longer, and “no specific origin” means the pain cannot be traced to any specific cause, incident, or injury.
Most susceptible are individuals who perform heavy physical work, especially when there is ongoing anxiety, depression, and emotional stress at the same time. The longer the stress and back pain continue, the more difficult it is to ease the symptoms and return the patient to normal functioning.
Treatment involves nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and sometimes opioid medications for pain, though both have risks when used long term. Antidepressants may also be tried, along with psychological counseling.
Corticosteroid injections for the back are effective for some patients, and fusion surgery is sometimes attempted. Lifestyle changes in the form of improved diet, exercise, and stress management are very helpful in most cases.
Rarity: Common
Top Symptoms: lower back pain, unintentional weight loss, back pain that shoots to the butt, fever, involuntary defecation
Symptoms that always occur with chronic low back pain of no specific origin: lower back pain
Symptoms that never occur with chronic low back pain of no specific origin: thigh numbness, buttocks numbness, lower back pain from an injury
Urgency: Primary care doctor
Don’t Miss: How To Determine Back Pain