What Is A Herniated Lumbar Disc
A herniated disc occurs when the gel-like center of your disc ruptures out through a tear in the tough disc wall .The gel material is irritating to your spinal nerves, causing something like a chemical irritation. The pain is a result of spinal nerve inflammation and swelling caused by the pressure of the herniated disc. Over time, the herniation tends to shrink and you may experience partial or complete pain relief. In most cases, if low back and/or leg pain is going to resolve it will do so in about 6 weeks.
Different terms may be used to describe a herniated disc. A bulging disc occurs when the disc annulus remains intact, but forms an outpouching that can press against the nerves. A true herniated disc occurs when the disc annulus cracks or ruptures, allowing the gel-filled center to squeeze out. Sometimes the herniation is so severe that a free fragment occurs, meaning a piece has broken completely free from the disc and is in the spinal canal.
Most herniated discs occur in the lumbar spine, where spinal nerves exit between the lumbar vertebrae, and then join together again to form the sciatic nerve, which runs down your leg.
What Is The Treatment For A Herniated Disc
conservativesurgeryphysical therapy including exercise
Spinal injections are also a non-surgical option. They may be recommended for short-term pain relief. Most people have relief from pain and other symptoms with conservative treatment.
Surgery is recommended for only a small number of people with herniated disc disease. It may be appropriate when a person continues to have severe or worsening pain or neurologic symptoms. There are both minimally-invasive and open surgery techniques.
As mentioned, exercise is a part of treatment for a herniated disc. The type and method of the exercise is important in order to support recovery and to avoid further injury.
There are many different exercises to help with back pain due to a herniated disc. We provide 5 effective ones. Also, you may know of other ways to perform these exercises. We provide one method for each.
How To Help Your Body Heal A Bulging Disc On Its Own
I dont want to get into the many, many reasons why long-term OTC and prescription drugs can be dangerous to your health.
increase the space between the vertebrae
This also helps to rehydrate the disc, which promotes the natural healing of the area.
This space increasing will also relieve your lower back pain. The pain is caused by this pressure on the nerves causing low back inflammation.
If you relieve the pressure, the pain is relieved. As simple as that.
This process is called spinal decompression .
It relieves the pain and allows your body to heal itself naturally Faster.
No medication, no surgery. And you can do spinal decompression at home by yourself, whenever you need it.
Read Also: Ibuprofen For Back Pain Dosage
Bridges Using Stability Balls
Stability or exercise balls are often used for exercising to manage the condition of herniated disc by strengthening the back. Here are the steps of using one such ball:
What Is A Slipped Disc
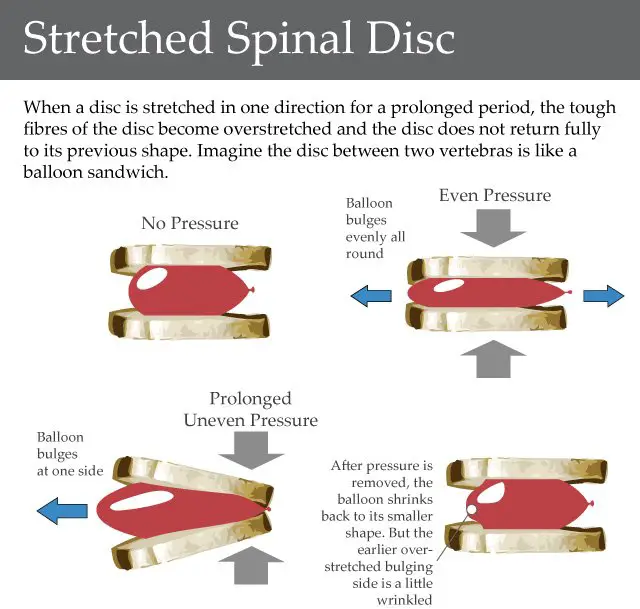
When you have a ‘slipped’ disc, a disc does not actually slip. What happens is that part of the inner softer part of the disc bulges out through a weakness in the outer part of the disc. A prolapsed disc is sometimes called a herniated disc. The bulging disc may press on nearby structures such as a nerve coming from the spinal cord. Some inflammation also develops around the prolapsed part of the disc. Inflammation may irritate a nerve and also causes swelling, which may put pressure on a nerve.
Any disc in the spine can prolapse. However, most prolapsed discs occur in the lower back . The size of the prolapse can vary. As a rule, the larger the prolapse, the more severe the symptoms are likely to be.
Also Check: Does Motrin Help With Back Pain
What Are Herniated Discs
As we said earlier, spinal discs separate each individual vertebra and soak up shock. Without them, the bones in your spine would grind against each another, and you’d be unable to absorb the impact of trauma and body weight.
More than just protective, these cushions also give the spine flexibility, making movements such as twisting and bending possible.
Like yin and yang, discs are both soft and hard at once. Theres a tough outer layer, called annulus fibrosus, and a soft, gel-like center, called nucleus pulposus. Fibers on the outside of each disc helps them attach to vertebrae and stay in place.
If the strong outer layer of the disc ruptures, the gel-like center can leak into the spinal canal: the passage that contains the spinal cord and spinal fluid. Pain strikes when that gel and potentially part of the outer disc and inner gel presses against the nerve roots that run along the spinal column.
The result can be intense pain in your back, along with weakness in an arm or leg. Numbness can also occur, since the nerve signals are being blocked. Making it all more troublesome is the fact that the gel can release a chemical irritant that may contribute to nerve inflammation and pain.
Herniated discs can compress nerve roots and even the spinal cord itself.
How Serious Is A Bulging Disc
Unlike a herniated disc, where the inner nucleus actually pushes through a tear in the outer annulus, a bulging disc happens when the entire disc changes shape and protrudes outward, into the spinal canal, but the annulus is still intact, and the nucleus remains inside the annulus.
As the disc is invading the space within the spinal canal, it can compress a nerve and cause a variety of issues felt throughout the body.
How serious a bulging disc is will depend on the degree of nerve involvement, location and severity of the bulging disc, not to mention other important variables such as patient age and overall health.
Common causes of a bulging disc are degenerative disc disease, poor lifestyle habits such as repeatedly lifting heavy objects with the back muscles, rather than the leg muscles, chronic poor posture, and carrying excess weight.
If a bulging disc is left untreated and worsens, it can easily become a herniated disc, so part of the focus of treatment for a bulging disc is to prevent it from becoming herniated.
So once a person is diagnosed with a bulging disc, what bulging disc treatment options are there?
Don’t Miss: How Does A Diuretic Help Back Pain
Physical Therapy Guide To Herniated Disk
Read Time:
A herniated disk occurs when the cushion-like cartilage between the bones of the spine is torn, and the gelatin-like core of the disk leaks. Often mistakenly called a slipped disk, a herniated disk can be caused by sudden trauma or by long-term pressure on the spine. This condition most often affects people aged 30 to 50 years men are twice as likely to be diagnosed as women. Repeated lifting, participating in weight-bearing sports, obesity, smoking, and poor posture are all risk factors for a herniated disk. The majority of herniated disks do not require surgery, and respond best to physical therapy. Physical therapists design personalized treatment programs to help people with herniated disks regain normal movement, reduce pain, and get back to their regular activities.
Physical therapists are movement experts. They improve quality of life through hands-on care, patient education, and prescribed movement. You can contact a physical therapist directly for an evaluation. To find a physical therapist in your area, visit Find a PT.
What Surgical Procedures Treat Herniated Discs
If you’ve tried non-surgical strategies and you still have symptoms after three months, surgery may be a good option. Its often a simple outpatient procedure that takes less than an hour.
“Spinal surgery has come a long way, even in the past few years. Unless there’s a concern, most people go home the same day, and usually in just a few hours after the procedure,” Dr. Anand says.
There are two main surgical procedures for a lumbar herniated disc.
Microdiscectomy
This procedure removes portions of the disc as a way to relieve the pressure on the spinal column. Microdiscectomy is sometimes called microdecompression.
Laminectomy
In a laminectomy, a portion of the vertebral bone is removed. This creates more space for the spinal cord and nerves, so they aren’t being compressed.
There are two additional options for herniated discs in the cervical spine
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion or cervical disc replacement
ACDF or CDR are both surgeries that remove the offending disc and insert either a bone graft or artificial disc to stabilize the area.
Microlaminoforaminotomy
In this surgery, your surgeon will remove a small piece of bone from your vertebra to create more space for the pinched nerve.
After either surgery, most patients feel relief from symptoms like pain, numbness, and weakness right away. However, it could take several weeks or months for the nerves to fully heal.
Recommended Reading: Aleve And Back Pain
How Is Lumbar Disk Disease Diagnosed
In addition to a complete medical history and physical exam, you may have one or more of the following tests:
-
X-ray. A test which uses invisible electromagnetic energy beams to produce images of internal tissues, bones, and organs onto film.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging . A procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body.
-
Myelogram. A procedure that uses dye injected into the spinal canal to make the structure clearly visible on X-rays.
-
Computed tomography scan . An imaging procedure that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce horizontal, or axial, images of the body. A CT scan shows detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs. CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays.
-
Electromyography . A test that measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerves stimulation of the muscle.
What Are Bulging Discs
Disc bulges are not quite the same as a disc herniation. Bulges are caused by the wear and tear of your spinal discs. These disks provide cushioning between the vertebrae, and when they are not in healthy condition, they can cause pain. According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons , the neck and lower back are the most common areas for disc bulges and herniations.
It can be difficult to tell, even by a medical professional, if you have a disc bulge, herniation or other abnormality. Healthy discs are contained inside their usual boundaries of the vertebral bone. If a disk is displaced with over 25 percent of the disc material protruding, then it is called a disc bulge, according to the North American Spine Society .
A disc herniation is diagnosed when 25 percent or less of the disc circumference is displaced. Interestingly, disc bulges are less painful on average than disc herniation, even though there is a more significant displacement, says the NASS.
To break it down further, a bulging disc results from a deformation without necessarily having a herniation. The disc nucleus is still inside the disc wall. When it comes to a bulging disc, you never need surgery to treat it, according to the South Carolina Spine Center .
Read more:Exercise Treatments for L4 and L5 Herniated Disc
You May Like: Does Aleve Help Back Pain
Causes Of Bulging Discs
While they can develop at any age, bulging disks are most common in people over the age of 30, and for reasons not totally understood theyre twice as common in men as in women.
Discs act like soft cushions that buffer the space between vertebrae, which are the small bones in the spinal column. Normally, discs serve as our natural absorbers of shock, allowing us to move around and remain flexible. In healthy adults, discs have a soft, gel-like center made up of flexible cartilage, surrounded by a tougher layer that keeps them held in place.
As someone becomes older, experiences more inflammation or becomes injured, the outer layer of the discs becomes more susceptible to being stretched, pulled or bulged out of the normal place they occupy. Once bulging, a disc becomes wider, stretched and also might become slightly squashed at the same time. Some experts say a bulging disc looks almost like a hamburger thats too big for its bun.
Growing pressure around a disc and poor posture are two common reasons why discs can start to bulge. When a normal disc experiences accumulating pressure, it starts to expand abnormally outward where it can come into contact with sensitive neural tissues. Eventually the bulging disc protrudes into the spinal canal, which is what triggers the sharp pain or tingling sensation thats associated with disc problems.
Bulging Disc Takeaways
Check If It’s A Slipped Disc

A slipped disc can cause:
- lower back pain
- numbness or tingling in your shoulders, back, arms, hands, legs or feet
- neck pain
- problems bending or straightening your back
- muscle weakness
- pain in the buttocks, hips or legs if the disc is pressing on the sciatic nerve
Not all slipped discs cause symptoms. Many people will never know they have slipped a disc.
Read Also: Advil For Lower Back Pain
Is A Bulging Disc Painful
discpainpainbulging discsA combination of the following conservative treatment options can be used through at least the first six weeks of discomfort and pain:
- Physical therapy, exercise and gentle stretching to help relieve pressure on the nerve root.
- Ice and heat therapy for pain relief.
- Manipulation
How To Prevent Bulging Discs
There are steps you can take at home to protect your spine and reduce the risk of disc injuries.
- Exercise. Regular exercise keeps your spine strong, healthy, and flexible. Focus on strengthening the muscles that support the spine: your core muscles, leg muscles, and low back muscles. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and yoga are an excellent way to stay active without overstressing the joints.
Also Check: Back Pain Advil
A Patient’s Guide To Lumbar Herniated Disc
Lower back problems can occur for many different reasons. The terms ruptureddisc and slipped disc seem to be used more commonly in the last few decades.People often assume that everyone who has back pain has a ruptured disc. However,a true herniated nucleus pulposus is not very common. Most problems that cause pain in the back are not due toa herniated disc.
For a more in-depth discussion of the parts of the spine and how they work,along with a general overview of back and neck problems, you might want to reviewthe document, entitled:
Let’s look at what a herniated disc really is, how it causes problems, and how the condition is diagnosed and treated by a back specialist.
Prone Lumbar Extension Or Half Cobra Stretch
This stretch is highly effective in moving the disc content back towards the middle of the intervertebral disc. This means it facilitates better recovery. As the focus is to extend the lower back, the repeated stretches aim at consolidating the radiating symptoms. In other words, the pain that reaches the leg and the foot withdraws to come back near the low back, which means ease of pain. Here are the steps of doing the half cobra stretch:
Slowly increase the upward position time to 30 seconds. Repeat the steps at least 10 times.
In the beginning, you might not feel comfortable or bear the stretch well. Thus, the key here is to begin gradually as well as carefully. In case you feel any pain, go for another variation or exercise.
Also Check: Aleve Good For Back Pain
How Are Herniated Discs Diagnosed
To figure out if you have a herniated disc, you can see an orthopedist or your primary care doctor. A herniated disc will be suspected if low back pain is accompanied by radiating leg pain.
Your doctor will likely have you do the straight leg raise test. Lying down, youll lift one leg straight up. If you have a herniated disc compressing on a nerve, that movement will increase the compression and cause pain throughout that leg. Your doctor will also ask about numbness, weakness, and slow reflexes.
From there, imaging studies are usually ordered. You may need:
Magnetic resonance imaging
This technology reveals the spinal cord, surrounding soft tissue and nerves. It is the best imaging study to support the diagnosis of a herniated disc.
MRIs are the diagnostic tool of choice for herniated discs because they can show soft tissue.
Nerve conduction studies and electromyogram
These studies use electrical impulses that measure how much your nerves might be affected by compression from a herniated disc. NCS and EMG are not routine tests to diagnose herniated disc, and are only used if you have symptoms of nerve trouble like numbness and radiating pain. These studies are typically only used if MRIs and a physical exam are inconclusive and your doctor thinks other conditions are a possibility.
X-Rays