Other Types Of Headaches
Sometimes migraines are misdiagnosed as sinus headaches. If you experience seasonal allergies youre more likely to develop sinus headaches.
Treatment options include thinning out the mucus that causes sinus pressure. You can use decongestants, nasal steroid sprays, and antihistamines.
If youre experiencing a sinus headache, it could be a sinus infection. Your doctor might prescribe you an antibiotic for your sinus infection.
Women can experience whats known as hormone headaches. These are caused by varying estrogen levels. Your estrogen levels can change if youre pregnant, menstruating, or taking birth control pills.
Pain All Over The Back Of The Head
Headache pain felt all over the back of the head is most commonly a tension-type headache. While nagging and unpleasant, tension-type headaches are not worrisome, and most can be eased fairly quickly.
Less commonly, headache pain generalized to the back of your head can indicate a more serious secondary headache, such as a low-pressure headache.
Tension Headaches Vs Migraines
How do you tell them apart?
Tension headaches:
- What do they feel like? Steady, mild to moderate pain that doesnât throb. It can ease or get worse over the course of the headache.
- Where do they hurt? It can hurt all over your head, but youâll most likely feel a band of pain around your forehead or the back of your head or around your neck. The headache does not get worse with activity. Your jaw, shoulders, neck, and head may also be tender.
- Are there any other symptoms? This type of headache doesnât come with the nausea, vomiting, light sensitivity, or aura that people with migraines have.
- Do you notice symptoms before the headache starts? You might feel stress or tension.
- Who gets them? Mostly adults.
- How often do you get them? It varies.
- How long do they last? Thirty minutes to 7 days.
Migraines:
Show Sources
Also Check: How Much Advil For Back Pain
Headache Back Of Head Due To Structural Disease Of The Junction Between Head And Neck
-
Chiari Malformation
The classic pain of Chiari Malformation is in the back of the head and is provoked by coughing, exertion, laughter or sneezing, so without these provoking factors a Chiari is less likely to be the cause.
-
Bulbocervical Cavernoma
Single case of severe pain in the back of the head associated with a vascular lesion in the upper spinal cord .
How Does A Dural Tear Occur

A tear in the dura may occur after a spinal tap or following spinal or epidural anesthesia.
A low-pressure headache is felt when sitting or standing up and is relieved within 20 to 30 minutes of lying flat. It’s usually also worsened when coughing, sneezing, or exercising.
Symptoms that may accompany a low-pressure headache include:
- Neck stiffness
- Double vision or blurry vision
Also Check: Does Aleve Work For Back Pain
Living With A Head Injury
Most people recover from head injuries with no lasting effects. However, damage can occur if your brain moves or is pierced. Talk to your doctor about how to manage side effects or symptoms, such as pain.
After a head injury, you may have memory loss. For example, you may forget the events right before, during, and after the accident. Memory of these events may or may not come back. Following treatment, the ability to learn and remember new things often returns.
Can Your Mind Create Physical Symptoms
So if you’re experiencing unexplained aches and pains, it might be linked to your mental health. According to Carla Manley, PhD, a clinical psychologist and author, people with mental illnesses can experience a range of physical symptoms, such as muscle tension, pain, headaches, insomnia, and feelings of restlessness.
Don’t Miss: How Much Advil For Back Pain
How Fainting May Cause Your Eyes To Roll Back
Fainting happens when you lose consciousness due to a sudden loss of blood flow to your brain. The medical term for fainting is syncope.
When someone loses consciousness, its possible that their eyes may roll back into their head before or when they fall down. Typically, an individual is only unconscious for a minute or two after theyve fainted.
Prior to fainting, you may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
The best way to immediately treat a fainting episode is to:
- move to a cool, quiet area
- lie down or sit down with your head between your knees
- drink some cool water
Most people recover from a fainting spell within a few minutes to hours. If your fainting is caused by a specific underlying condition, your doctor will work to treat that.
When To Worry About A Headache
Are you currently suffering from headaches? You may treat headaches as a common occurrence and just grab painkillers over the counter. And youre not alone since up to 1 in 20 adults have a headache every day. However common they may be, there are key signs indicating when you should be worried about your headache.
You May Like: Aleve And Back Pain
How Epilepsy May Cause Your Eyes To Roll Back
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition that causes unprovoked, recurrent seizures. Youre typically diagnosed with epilepsy when youve had two or more seizures that cant be explained by an existing medical condition.
Seizures due to epilepsy fall into two broad categories generalized and focal. People with epilepsy can experience both types.
Generalized seizures affect both hemispheres of the brain while focal seizures impact a specific area. Within each type of seizure, there are also many further subtypes.
The specific symptoms of a seizure can vary, depending on the type of seizure it is. With some types of generalized seizures, such as absence seizures, the eyes may roll back into the head.
When To Seek Medical Attention
In addition to the more problematic causes outlined above, headaches can also be the result of many benign causes, so it is easy to mistake something serious for something mild or vice-versa. A few general rules of thumb:
- Any severe headache that suddenly appears without warning or discernable cause should be brought to your doctors attention and needs to be checked out
- Persistent or recurrent headaches that undergo a change in frequency, severity, or steadily worsen should warrant a consult with your doctor
- Headaches that accompany red eyes, physical injury, visual disturbances , or cognitive/personality changes deserve immediate medical attention
Also Read:
Read Also: How Much Advil For Back Pain
How To Prevent Positional Headaches
There is no way to fully prevent positional headaches from developing, as they are generally caused by underlying medical conditions.
However, you may reduce the risks of conditions that cause these headaches by practicing healthy lifestyle habitssuch as eating a well balanced dietand avoiding unnecessary muscle strain.
Risk factors for developing a CSF leak include:
- Overexerting or straining muscles during physical activity
- Frequent fits of extreme coughing or sneezing
- Engaging in activities that jolt or lurch the body around
- Undergoing certain medical procedures, such as a lumbar puncture
- Genetic or hereditary conditions, including polycystic kidney disease
- Tumors or cysts in the head, neck, and spine
There is a greater risk of developing POTS in people who:
- Suffer from an autoimmune condition
- Have recently experienced mono, or a serious infection or virus
- Have recently suffered a traumatic head injury
- Are or were recently pregnant
There Are Two Main Types Of Headachesand Location Does Matter When Identifying Them
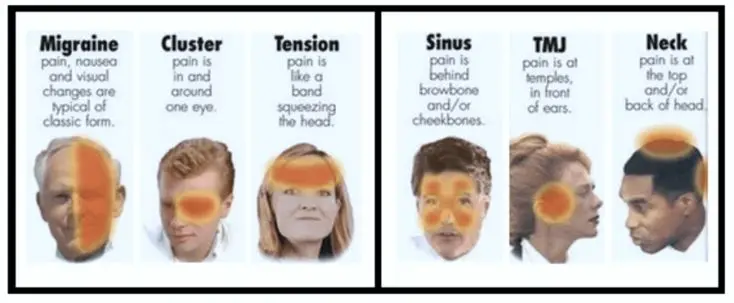
Most headaches fall into one of two categoriestension or migraineand the location of your pain is one tactic for distinguishing between them. “Tension type headaches tend to be more mild, are on both sides of the head, and are often described as dull pressure or a band around the head,” says Dr. Hamilton. “Migraines tend to overall be more severe.” They’re typically one-sided and culminate in a more throbbing, pulsing painand have other unfortunate symptoms, like nausea or light sensitivity, she says. And while there is a third type, it’s far less common: Cluster headaches always happen on the same side of the head, behind your eye.
Common triggers of tension headaches and migraines include dehydration, illness, not getting enough sleep, hormonal changes, skipping meals, and stressbut those don’t cause a headache in one specific location. “When we’re diagnosing headaches, we take into account triggers,” says Dr. Hamilton, “but there’s not a headache due to dehydration specifically, or a headache due to sleep deprivationthose would be lumped into the migraine or tension-type.”
Read Also: Back Pain Cleveland Clinic
What Is A Positional Headache
A positional headache is characterized by pain in the back of the head that begins or worsens when standing up or sitting, and is eased or alleviated by lying down .
Other names for a positional headache include:
- Orthostatic headache
- Postural headache
- Low pressure headache
If you are still experiencing a headache when lying down for 30 minutes or longer, you likely are not suffering from a positional headache. You may be suffering from a tension headache, migraine, or other common type of headache.
Head Pain Has Other Causes
Not all head pain is diagnosed as a tension headache or migraine, though, and in those cases, the location can offer important information about other causeslike muscle tension, nerve pain, or jaw issues. “Oftentimes, headaches related to muscle tension can cause pain in certain areas,” notes Dr. Hamilton. Dull pain by your temples, especially when you wake up in the morning, could indicate teeth clenching or TMJ a headache in the back of your head and along your neck may be related to neck tension or a cervical spine issue. Nerve irritation can also cause pain in one spot: “There are different nerves around the head, and if you’re having a specific type of pain over a focal area, that can be indicative of irritation of the local nerve,” she adds. “For example, there are big nerves in the back of the had called occipital nerves, and sometimes those can get irritated and present with sharp shooting pains in the back if the head. If the pains really are limited to that distribution of the nerve, that can be a sign of local irritation.”
Read Also: How Does A Diuretic Help Back Pain
How K Health Can Help
Positional headaches are fairly easy to identify. Did you know you can get affordable primary care with the K Health app? Download K to check your symptoms, explore conditions and treatments, and if needed text with a doctor in minutes. K Healths AI-powered app is HIPAA compliant and based on 20 years of clinical data.
K Health articles are all written and reviewed by MDs, PhDs, NPs, or PharmDs and are for informational purposes only. This information does not constitute and should not be relied on for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
What Is Causing My Neck Pain And Headache
See Understanding Neck Pain and Dizziness
Several conditions can cause neck pain and headache. Some conditions may start as a neck problem and then send symptoms up to the head, whereas other conditions begin in the head and send pain down to the neck. Getting an accurate diagnosis is important in order to create a treatment program to successfully manage the condition and reduce pain.
Read Also: Is Motrin Good For Back Pain
Symptoms Of A Head Injury
With a head injury, its normal to have a headache and nausea. You may be dizzy or disoriented right afterward. You also may have problems focusing or remembering. Other symptoms include ringing in your ears, neck pain, or vision problems. These symptoms often go away in a few weeks, but may last longer if the injury is severe.
Get help right away if you notice the following:
- Any symptom that gets worse, such as headaches, nausea, or fatigue.
- Frequent vomiting.
- Seizures.
Occipital Neuralgia And Pain At The Base Of Skull
A sharp jabbing pain that feels like an electric shock at the back of your head could be a symptom of occipital neuralgia. You may also find that your scalp is tender to touch and even a simple task like brushing your hair can cause pain. This type of pain can be caused by inflammation in the nerves at the back of your head.
The American Association of Neurological Surgeons says that occipital neuralgia causes pain in the base of skull which usually radiates to just one side of the head, but can often be felt on both sides of the head.10
To help ease the pain caused by occipital neuralgia, AANS recommends using gentle heat treatments and rest for headache relief. A soothing massage can also help to get rid of the headache pain caused by occipital neuralgia. You can also use essential oils to relieve the pain.
Doctors treat occipital neuralgia and migraines differently, so its important to know your symptoms to get the appropriate treatment for your headaches.
Read Also: Will Naproxen Help Back Pain
How To Eliminate Your Tension Headache
Ensure you are up to date with you eye examinations.
Whether that is having your first eye examination or booking in for a review if it has been over two years since youve last been for one.
Check your workstation!
You should not be slouching into your chair or leaning forward to reach the screen. Your feet should be flat on the ground with a 90-degree angle from your hips to your knees. You should aim to rest your elbows on the armrests or table and aim to keep your back straight and supported. If in doubt, ask for a desk assessmentfrom your employer.
Keep your neck and head as mobile as possible
Try and take regular breaks as this encourages you to naturally move your head and spine. This also prevents muscles from tightening up.
Introduce yoga or meditation
These activities can help rid any tension headaches which may be caused by stressed.
In addition to this, adopt a lifestyle which is beneficial to your health. This includes getting enough sleep, not smoking, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy and balanced diet. Finally, remember to drink plenty of water and limit your alcohol, caffeine, and sugar intake.
Reach out for help
If youre experiencing a niggling pain that wont go away, then book in to see one of our expert Bodyset physiotherapists. Were here to help you get the best out of your body so you can get back to doing more of what you love.
Not sure you need to see a physiotherapist for a full assessment?
How Can I Prevent Headaches

The key to preventing headaches is figuring out what triggers them. Triggers are very specific to each person what gives you a headache may not be a problem for others. Once you determine your triggers, you can avoid or minimize them.
For example, you may find that strong scents set you off. Avoiding perfumes and scented products can make a big difference in how many headaches you have. The same goes for other common triggers like troublesome foods, lack of sleep and poor posture.
Many people, however, are not able to avoid triggers or are unable to identify triggers. In that case, a more personalized multidisciplinary approach with a headache specialist is often necessary.
Read Also: Exercise For Lower Back Pain Mayo Clinic
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
POTS is a condition affecting the autonomic nervous system , hindering the ANS from doing its normal job which is to properly regulate heart function and balance of bodily fluids.
A person with POTS will generally experience spikes in heart rate when switching from a lying or sitting position to standing up. This causes symptoms of dizziness, sudden fatigue, or headache upon standing.
These symptoms may be accompanied by:
- Lightheadedness
- Diarrhea
- Swelling in the lower legs and feet
It is unclear exactly what causes POTS, though the majority of cases are seen in women between 15-50 years old.
When To Get Medical Help For A Headache On The Back Of Your Head
You should get medical help immediately if you have a headache on the top of your head or in another location on your head and you experience any of the following:
- the headache changes, gets worse quickly or is severe
- the headache doesnt go away
- youve recently injured your head
- you coughed, sneezed or moved suddenly or quickly and this triggered your headache
- you have a weakened immune system, for example if youre undergoing chemotherapy
- youre pregnant
- you may have been exposed to carbon monoxide
- you think you have a migraine but are worried by other symptoms
You should also get immediate medical help if you have a headache and:
- you have a high temperature
- youve had a fit
- you feel confused or dizzy
- any of your limbs feel weak
- your eyes are sensitive to light
- youve noticed changes in your personality, speech or vision
- you have a stiff neck
- youre being or have been sick
If none of the above applies, your headache may be caused by one of the reasons below.
You May Like: Aleve Lower Back Pain
Pain In The Neck And Back Of The Head
Arthritis
Arthritis headaches are caused by inflammation and swelling in the neck area. They often cause pain in the back of the head and neck. Movement typically triggers more intense pain. These headaches can be caused by any kind of arthritis. The most common are and .
Poor posture
Poor posture can also cause pain in the back of your head and neck. Poor body positioning creates tension in your back, shoulders, and neck. And that tension may cause a headache. You may feel a dull, throbbing pain at the base of your skull.
Herniated disks
Herniated disks in the cervical spine can cause neck pain and tension. This can cause a type of headache called a cervicogenic headache.
The pain typically originates and is felt in the back of the head. It may also be felt in the temples or behind the eyes. Other symptoms may include discomfort in the shoulders or upper arms.
Cervicogenic headaches may intensify when youre lying down. Some people will actually wake up because the pain disrupts their sleep. When lying down, you may also feel a pressure on the top of your head like a weight.
Occipital neuralgia
Occipital neuralgia is a condition that occurs when the nerves that run from the spinal cord to the scalp are damaged. It is often confused with migraines. Occipital neuralgia causes sharp, aching, throbbing pain that starts at the base of the head in the neck and moves towards the scalp.
Other symptoms include:
- watering eyes
- light or sound sensitivity