Nonsurgical Treatment For Osteoarthritis Of The Spine
If osteoarthritis of the spine is diagnosed early, doctors may recommend nonsurgical treatment to manage symptoms. NYU Langone physicians, physical therapists, and physiatrists, who specialize in rehabilitation medicine, can help you relieve pain and stiffness, improve flexibility, and build strength in muscles that support the spine.
These treatments do not reverse damage to cartilage or bone or prevent the progression of osteoarthritis, but they may make it possible for you to continue an active lifestyle.
Can I Prevent Lower Back Pain
You cant prevent lower back pain that results from disease or structural problems in the spine. But you can avoid injuries that cause back pain.
To reduce your risk of a back injury, you should:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts pressure on vertebrae and disks.
- Strengthen your abdominal muscles: Pilates and other exercise programs strengthen core muscles that support the spine.
- Lift the right way: To avoid injuries, lift with your legs . Hold heavy items close to your body. Try not to twist your torso while youre lifting.
Spinal Arthritis May Contribute To Other Issues In The Spine
Spinal arthritis may cause bone spurs overgrowths on the edges of the bones. In the spine, bone spurs particularly affect facet joints, making them grow larger. This condition is called facet joint hypertrophy. Although bone spurs on their own are not harmful, they may narrow the passages for the spinal cord and the nerves exiting the spine. This may lead to two painful conditions:
-
Spinal stenosis compression of the spinal cord inside the spinal canal
-
Radiculopathy pinching of the peripheral nerves as they exit the spine
Ankylosing spondylitis may also cause additional problems such as:
-
Stress fractures in places where new bone has formed
-
Collapsed vertebrae
-
A spinal deformity called kyphosis
You May Like: Advil For Back Pain Dosage
Progression Of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Over months or years, pain may spread up the spine and into the neck. As the disease progresses, the body’s defense mechanisms fight back by producing new bone . The new bone grows between and around the vertebrae, causing abnormal fusion and increases the risk for spinal fracture.
Sometimes ankylosing spondylitis leads to a spinal deformity such as a humpback or swayback . Advanced symptoms can be chronic and include severe pain and stiffness of the spine and possibly other body joints. Bowel and eye inflammation may be associated with ankylosing spondylitis.
How Is Osteoarthritis Of The Spine Diagnosed
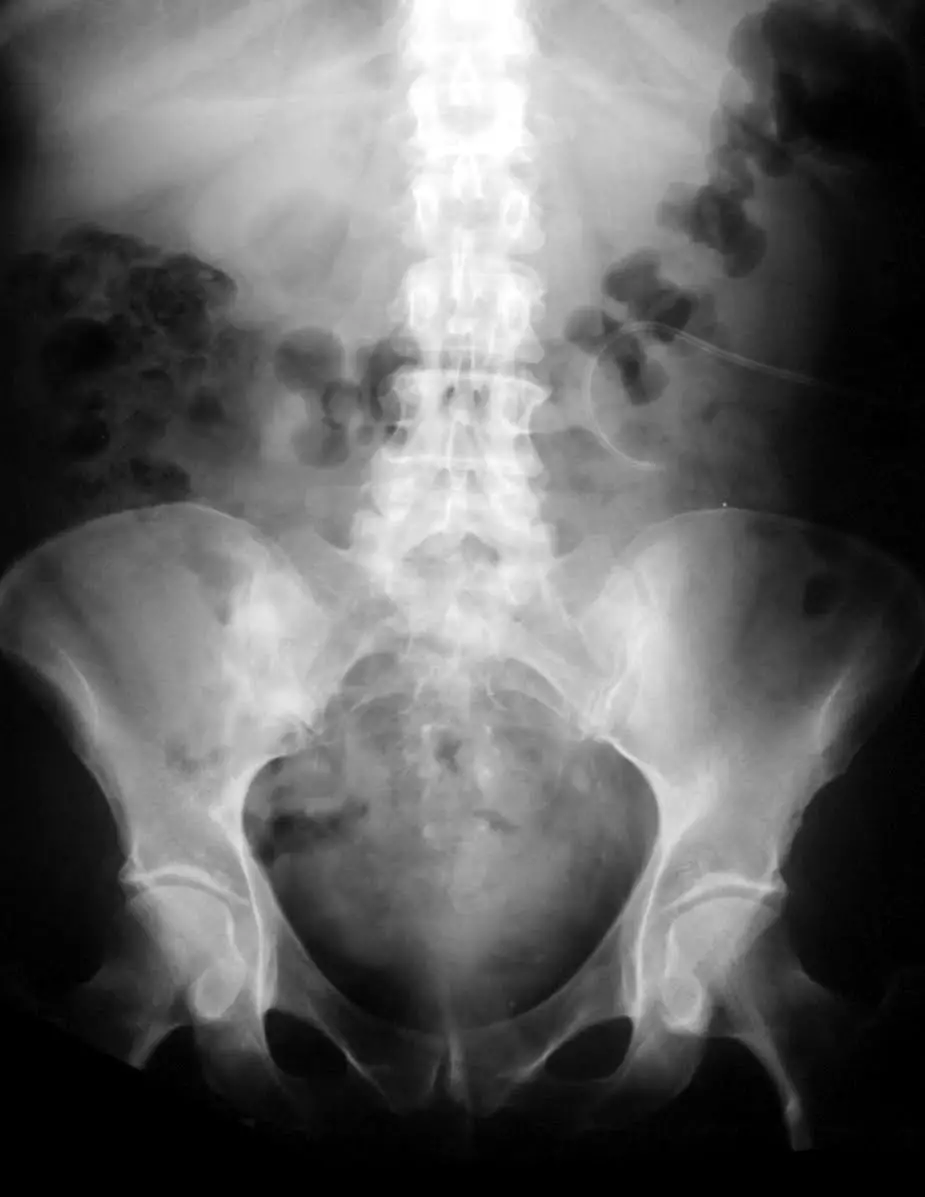
The best way to confirm a diagnosis of osteoarthritis is by X-ray. The doctor will take a medical history and perform a physical exam to see if the person has pain, tenderness, loss of motion involving the neck or lower back, or if symptoms are suggestive, signs of nerve involvement such as weakness, reflex changes, or loss of sensation.
The doctor may order certain tests to aid in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the spine. These tests include:
- X-rays to look for bone damage, bone spurs, and loss of cartilage or disc however, X-rays are not able to show early damage to cartilage.
- Blood tests to exclude other diseases
- Magnetic resonance imaging to show possible damage to discs or narrowing of areas where spinal nerves exit
Recommended Reading: Back Pain Advil
What Are The Different Types Of Arthritis That Affect The Back
There are several types of arthritis. The different types of arthritis that may affect the back or neck include
- Osteoarthritis of the spine: This is noninflammatory, degenerative arthritis. It is the most common form of arthritis that affects the back. Wear and tear seem to be the reason that osteoarthritis develops.
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the spine: This is an autoimmune disorder where the lining of the joints is affected. Its a type of inflammatory arthritis because wear and tear on the joints is not involved.
- Fibromyalgia: This causes chronic, widespread muscle pain and fatigue.
- Spondyloarthritis: This is a group of inflammatory diseases that affects both the joints and the areas where the ligaments and tendons are attached to the bones. There are several forms of spondyloarthritis, including
- Ankylosing spondylitis: This is a type of spinal arthritis that causes inflammation of the vertebrae and the joints at the base of the spine.
- Psoriatic arthritis: This is an autoimmune disorder triggered by psoriasis and it is characterized by an itchy, scaly rash.
- Reactive arthritis: In this type of arthritis, a gastrointestinal or genital infection probably triggers joint inflammation. It usually affects the lower back.
- Enteropathic arthritis: This is a type of arthritis linked to inflammatory bowel disease.
- Undifferentiated spondyloarthritis
What Causes Osteoarthritis
The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, is associated with injuries, wear-and-tear processes, and genetics. An arthritis joint will demonstrate the narrow bone spaces due to various reasons. The cartilage thins, the formation of cysts within bones, bones spurs seen on the edges, deformity of joints are some of the reasons, which leads to crooked joints.
*All individuals are unique. Your results can and will vary.
You can get rid of joint pain instantly by browsing through the best joint supplement reviews on the market. Read them carefully to arrive at the decision of buying the best product on the market.
Recommended Reading: Aleve For Lower Back Pain
How Is It Diagnosed
Your physical therapist will perform a thorough evaluation and ask you questions in order to form a clear picture of your individual situation. These questions may include:
- Your past and current health and use of medication.
- How you are functioning in your daily life.
- How your symptoms came about.
- How long you have had symptoms.
- Where the symptoms are located.
- How and when pain occurs.
Your physical therapist will then conduct a physical examination and may:
- Evaluate your posture and measure the range of motion of your spine.
- Assess the movement of the spine and extremities in the involved area.
- Check your nerve function with reflex, sensation, and strength testing.
- Observe how you move during commonly performed activities.
- Check your balance to determine your risk of falling.
The information learned in your evaluation will help your physical therapist prescribe a program to ease your discomfort, boost your quality of life, and get you moving your best.
If your physical therapist suspects that your pain might be caused by an underlying condition, they may request imaging testing such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI from your doctor. Your therapist may also refer you to your doctorfor further evaluation. Your physical therapist will work with your doctor to provide the best diagnosis and treatment.
Osteoarthritis Of The Back/spine
Spinal OA can make it hard to get around. Treatment can ease your back pain.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis that affects the back. It can occur anywhere along the spine. Usually the low back and sometimes the neck are affected.
In OA, the cartilage that pads the ends of the bones wears down. In spinal OA, this occurs in the facet joints small joints located between and behind vertebrae.
When you move, the bones rub together painfully. Bony growths form in the joints. These spurs can press on nerves, causing more pain.
Causes of Back/Spine OA
The cause of OA is unknown. Some common factors that play a role in OA include:
- Age: The older you are the greater your chance of having OA.
- Weight: People who are overweight are more likely to have OA.
- Stress: Repeated joint stress from work or sports can increase your risk.
- Injury: A back injury can lead to OA.
- Genetics: Some people have a family history of OA.
Symptoms of Back/Spine OA
Symptoms usually start slowly and get worse as time goes by. Pain and stiffness may be worst when you first wake up or after sitting for a long time. Pain can also get bad after being very active.
- Stiffness and a loss of flexibility: Turning your neck or straightening your back may be tough.
- Pain: Your low back is the most common site of pain.
- Crepitus: You may have a feeling of grinding when moving.
- Tenderness and swelling: Your back along the affected joints may be sore to the touch.
Diagnosing Back/Spine OA
Non-Drug Treatments
Read Also: Mayo Clinic Low Back Pain Exercises
Reasons For The Procedure
X-rays of the spine, neck, or back may be performed to diagnose the cause of back or neck pain, fractures or broken bones, arthritis, spondylolisthesis , degeneration of the disks, tumors, abnormalities in the curvature of the spine like kyphosis or scoliosis, or congenital abnormalities.
There may be other reasons for your health care provider to recommend an X-ray of the spine, neck, or back.
Back in the Saddle After Spinal Surgery
Anne Fink made spinal surgery look like a walk in the park, but she will be the first to tell you its because of Johns Hopkins spine surgeon Khaled Kebaish. Thanks to him, Im a walking medical miracle. He gave me my life back, she says.
Muscle Strain Or Sciatica
Muscle strain is often the cause of back pain from heavy lifting or vigorous exercise. But sometimes itâs due to small jelly-filled disks meant to protect the space between vertebrae. When one of these disks bulges or breaks, it can push on a nerve. When itâs the sciatic nerve, pain runs from the buttock down one leg. This is sciatica.
Read Also: Will Aleve Help With Back Pain
Exercise For Arthritis In The Neck
Physical therapy
If youre experiencing neck pain due to arthritis, your doctor may recommend physical therapy. Physical therapy for neck arthritis entails doing specific exercises to help strengthen and stretch weak or strained muscles. Physical therapy can improve range of motion. Sessions and programs vary in length and frequency and are tailored to your condition.
The foundation of what were trying to do in physical therapy for the neck is often to help improve posture and the way people move, says Dr. Milani. Exercises in physical therapy tend to be focused on strengthening muscles of the back and neck, which puts less strain on structures of the cervical spine.
Youll do exercises during physical therapy and get instructions on ones to do at home.
Regular Physical Activity at Home
You may feel like you dont want to move when your neck hurts. But being inactive may increase stiffness, which can cause you to lose even more mobility. Aches and pains tend to respond better to continued movement than rest, says Dr. Milani. Exercise is often the foundation of treatment.
Exercises that involve stretching, strengthening, and improving range of motion can help reduce pain and keep your neck limber. You want to move gently and smoothly when doing neck exercises, not jerk your neck or make sudden movements. You may feel discomfort at first. Stop if any exercise increases your neck pain.
Spondyloarthritis In The Neck
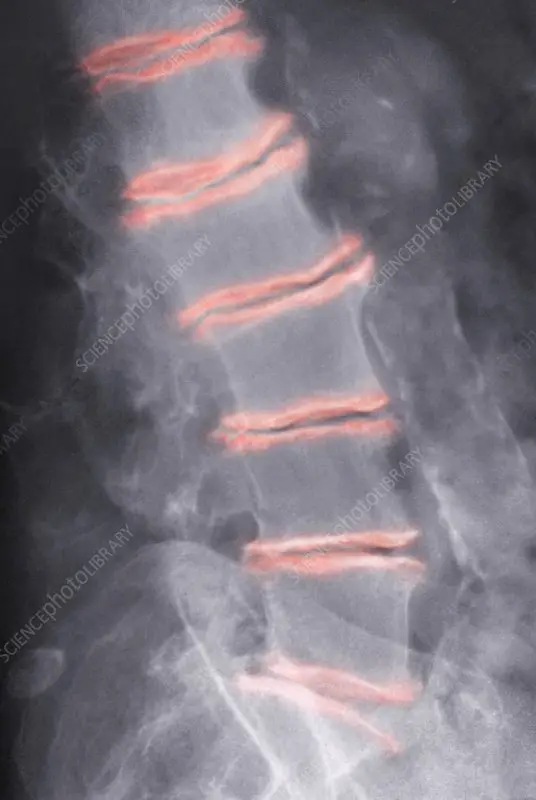
Other types of neck arthritis include psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, which are both considered a type of arthritis called spondyloarthritis. Its an umbrella term for inflammatory diseases that involve both the joints and entheses, the places where ligaments and tendons attach to the bones.
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of arthritis often accompanied by psoriasis, an inflammatory skin disease. For some people who have psoriatic arthritis, the condition involves the spine, which impacts the neck. Pain happens when inflammation strikes the joints between the vertebrae. This pain can occur on just one side of the body, the neck, and the lower and upper back. Read more about psoriatic arthritis symptoms.
Ankylosing spondylitis is a form of arthritis that strikes the bones in your spine and pelvis as well as peripheral joints. Early signs and symptoms might include pain and stiffness in your lower back and hips, especially in the morning and after inactivity. Fatigue and neck pain are common. AS symptoms might worsen, improve, or stop at irregular intervals.
Also Check: Advil For Lower Back Pain
What Are Some Of The Other Methods To Diagnose Osteoarthritis
Besides the appearance of arthritis on X-ray, there are some other tests as well that are performed by the doctors to know better about the patients condition. Before the X-Ray test, the doctor will ask some questions to study your symptoms. The doctors will ask these things to the patient.
- The degree of pain
- How long have you been suffering from this pain?
- What kinds of activities are difficult to perform because of the pain or decreased mobility?
After reviewing the symptoms, the doctor will perform some physical examinations to know about these things:
- See if there is a swelling in the joint, as it could be a sign of excess fluid.
- Check if the muscle is thinning or not
- Check out joint mobility to see if it is normal or not
- Joint tenderness
- The grating sounds while moving the joints, which is called crepitus
- Swelling in the bones
- Joint instability
Some other forms of tests that doctors may include are as follows:
- Blood tests: The blood tests are usually not necessary to diagnose osteoarthritis however, the doctor may ask the patient to test their blood for ruling out other possible diagnoses.
- Joint fluid analysis: The doctor will use the needle for withdrawing the fluid if there is an excess swelling around the joints. The fluid will be used by the doctor to see if the patient has an infection, gout, or some osteoarthritis-related inflammation.
How Arthritis In The Back Is Diagnosed
Diagnosing arthritis in the back begins with taking your medical history and doing a physical exam of your back and legs to assess your mobility/flexibility and make sure your nerves are working properly. The doctor will ask questions about:
- Where the pain is occurring
- How long the pain has lasted
- What the pain feels like/how severe it is
- What situations/activities make the pain feel better or worse
- How the pain is affecting/limiting your daily function
Imaging tests are usually needed to help confirm a diagnosis of arthritis. X-rays are typically the first imaging test ordered. They can joint damage/bone spurs, but cannot show damage to soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, or bulging discs. Other tests may be ordered to look for changes or damage that is not visible on X-rays. These may include MRI, CT, ultrasound, bone scans, or other tests as needed. The gold standard to diagnose arthritis in the back is actually an injection called a medial branch block, but its not often necessary, says Dr. Kirschner.
If your doctor suspects you could have a type of inflammatory arthritis, they may order blood tests to look for signs of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Other blood tests may look for genetic markers associated with axial spondyloarthritis, such as HLA-B27, or antibodies associated with rheumatoid arthritis .
Recommended Reading: Does Aleve Help With Back Pain
Spinal Arthritis: What You Need To Know
-
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis to affect the spine.
-
Arthritis can occur anywhere along the spine, but is more frequent in the lower back and neck.
-
Pain and stiffness are the most common symptoms of spinal arthritis.
-
Causes of spinal arthritis are still largely unknown except for osteoarthritis, which is typically a result of wear and tear.
-
Spinal arthritis treatment may include pain medications, steroid injections, physical therapy and surgery in severe cases.
What Are The Symptoms Of Lower Back Pain
Symptoms of lower back pain can come on suddenly or appear gradually. Sometimes, pain occurs after a specific event, such as bending to pick something up. Other times, you may not know what caused the pain.
Pain may be sharp or dull and achy, and it may radiate to your bottom or down the back of your legs . If you strain your back during an activity, you may hear a pop when it happened. Pain is often worse in certain positions and gets better when you lie down.
Other symptoms of lower back pain include:
- Stiffness: It may be tough to move or straighten your back. Getting up from a seated position may take a while, and you might feel like you need to walk or stretch to loosen up. You may notice decreased range of motion.
- Posture problems: Many people with back pain find it hard to stand up straight. You may stand crooked or bent, with your torso off to the side rather than aligned with your spine. Your lower back may look flat instead of curved.
- Muscle spasms: After a strain, muscles in the lower back can spasm or contract uncontrollably. Muscle spasms can cause extreme pain and make it difficult or impossible to stand, walk or move.
You May Like: Aleve And Back Pain
Surgery For Neck Arthritis
Surgery is usually a last resort for neck arthritis, says Dr. Milani. Your doctor may recommend it if you have severe pain that isnt relieved with nonsurgical treatment or if you have signs of neurologic injury. Surgery may be needed if the arthritis causes instability, or more importantly, impingement of nerves and/or the spinal cord, says Dr. Shah.
Changes Visualized Through Imaging
Physicians, such as rheumatologists, use several different forms of imaging techniques to monitor AS disease progression. For instance, X-rays can be used to visualize malformations of the spine. X-rays, also called radiographs, use radiation to take pictures of bones and other materials that are harder than soft tissue, like skin and organs. Magnetic resonance imaging is also used.
Radiography is the conventional method for assessing structural damage in spine and sacroiliac joints in individuals with AS. MRI has gained a prominent role in monitoring disease activity during clinical trials and regular clinical practice. Radiography and MRI are useful in monitoring the disease progression of AS and can complement each other well when used together.
Erosion and ankylosis of the sacroiliac joints are the hallmarks of AS, and X-rays are commonly used to visualize disease progression in this area of the body. Additionally, early radiographic signs of AS in the spine are most often due to inflammation .
Computed tomography and ultrasonography are also sometimes used, but each have their drawbacks. For example, CT scans use large amounts of radiation and do not assess damage to soft tissues well.
Also Check: Does Motrin Help With Back Pain