Back Pain In Youth Athletes: Is It Serious
Everyone is outside again, playing sports and having fun in warmer weather. As spring sports seasons progress, I always see an increase in injuries and pain.
As director of Sports Medicine at Cincinnati Childrens, I see many young athletes in clinic who have new back pain related to their sport. Up to 30% of athletes will have back pain at some point while playing sports. It is one of the most common things we see in sports medicine clinics and on the sideline.
Most back pain is not serious and goes away with little treatment. Gently stretching and strengthening the lower back and abdominal muscles, as well as avoiding activities that are really painful for the back, is usually all it takes.
But, when the pain is severe, limits what the athlete can do, or persists for more than a few weeks, a doctor with specialized training in back injuries should evaluate the athlete to determine the cause of the pain and treat it accordingly.
Lower back pain
The lower back, or lumbar spine, is the most common area of back pain in athletes. Pain usually occurs from bone, muscle or disc problems. The most common cause of lower back pain in young athletes is a stress fracture-a bone injury. The second most common cause is a muscle strain of the lower back.
Treatment and Recovery
Treatment of a lower back stress fracture involves 2-3 months of allowing the bone to heal, just like any other broken bone. Various types of imaging are sometimes done to help guide treatment course.
Characteristics Of Back Pain In Teens
Different causes have their own characteristic features which are as follows:
How Is Spondylolysis Diagnosed
Health care providers will do an exam. They might push on the back or ask a patient to bend backward to hyperextend the spine. If these things cause back pain, it’s possible that there’s a fracture in the pars, a specific part of the spine bone.
Other things, such as muscle pain, a pinched nerve, or herniated disc, also can cause lower back pain. To rule those out or to confirm a diagnosis of spondylolysis health care providers may order tests such as:
- a back X-ray to look for fractures
- a bone scan or a CT scan, which can detect smaller fractures
Also Check: Advil Vs Ibuprofen For Back Pain
What Treatment Options Are Available For A Child With Back Pain
In many children, back pain is short-lived and settles down without treatment. Studies have found that this happens in about half of all teenagers with back pain, and it’s usually due to over-enthusiastic sporting activities or the use of backpacks.
If the back pain is persistent it’s important to investigate the cause. Simple painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen may help. Your child may be referred to a physiotherapist who will advise about any changes which can be made to your child’s lifestyle to relieve the pain and stop it from happening again. They may also provide various forms of physical treatment and advise a course of exercises that can be done at home,.
If your child’s pain lasts longer than 4-6 weeks, is getting worse, or is accompanied by unusual features such as a persistent high temperature or numbness, they may be referred to a specialist. If there is a serious cause, it is usually important to start treatment as soon as possible. The treatment advised by the specialist will depend on the cause.
Back Pain In Teenage Athletes: When To Worry
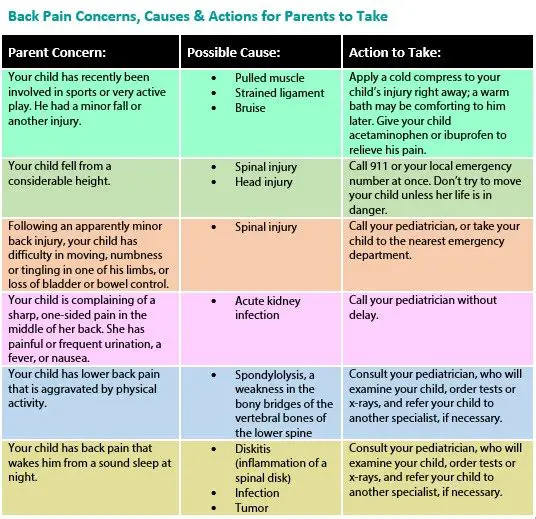
Teenage athletes often have strong and healthy bodies that resist injury with ease. However, back pain remains a common problem in many teen athletes’ lives and may indicate a more serious issue. Therefore, parents of teenage athletes need to know what issues connect with back pain and how to treat this concern.
Don’t Miss: Will Aleve Help Back Pain
Lumbar Strain: The Heavy Weight Was Too Heavy
Lifting weights youre not trained for, combined with a bad form, can cause serious health issues. Lumbar strain is an injury to your lower back. The muscles that stabilize your spine can be stretched too far, which causes tiny tears on the tissue. Consequently they get weaker, not supporting your spine correctly, and make it less stable and painful.
Symptoms differ from sudden pain, spasms, sever pain, stiffness and soreness. Back support brace can help with easing the pressure, stabilization, keeping the back warm and relieving the pain. In any case, seek medical treatment for further diagnosis.
You can only reach your full potential if your back works with you. When using a back brace you increase blood flow and working temp is quicker reached. Blood lactate level is lowered much faster due to warmth and compression, by a back brace.
Johan Bolin, Product Developer of Rehband products and Physiotherapist, Otto Bock Scandinavia AB.
The Most Common Causes Of Lower Back Pain Are A Strain Or Sprain
Whether you notice it or not, your lumbar spine gets put to work throughout the entire day.
Amid all of this work and motion, a lower back sprain or strain can result from an acute injury, such as one experienced while falling, lifting something too heavy or playing sports. A sprain or strain can also develop over time due to repetitive movements or poor posture.
“Straining a muscle or spraining a ligament are the most common causes of lower back pain,” says Dr. Palmer. “While they can be serious, these common causes of lower back pain aren’t long-lasting taking anywhere from a few days to heal or, at most, a few months.”
Your doctor can help you determine the particular course of self-care that can help heal your lower back pain.
“The treatment for a pulled back muscle or strained back ligament is fairly simple and can include pain and anti-inflammatory medications, muscle relaxers, ice to help reduce inflammation, heat to promote healing, and avoiding strenuous activity until the pain recedes,” explains Dr. Palmer. “The best course of care will depend on the severity of your injury as well as your overall core and lower body strength.”
If your lower back pain persists despite treatment, it may be time to consider other causes of lower back pain.
Also Check: Advil Good For Back Pain
Lower Back Pain Causes: 8 Reasons For Sudden & Chronic Pain
Sometimes, you know exactly why your back is hurting. Maybe you lifted something awkwardly and felt the pain right away. Or maybe your doctor has been warning you for years that your bad posture would lead to lower back pain.
But other times, the source of back pain can feel like a mystery.
“Your lumbar spine, located in your lower back, plays a crucial role in supporting the weight of your upper body. It’s also responsible for everyday movements, such as bending, twisting and coordinating the muscles in your hips, pelvis legs and feet,” says Dr. Kenneth Palmer, orthopedic surgeon specializing in spine surgery at Houston Methodist. “Due to heavy use, the bones, muscles, ligaments, disks and nerves found in your lumbar spine are quite susceptible to both injury and wear and tear over time causing pain in the lower back.”
Lower back pain symptoms include:
- Dull ache in your hips and/or pelvis
- Muscle spasms or tightness
- Sharp, tingling pain that starts in your lower back and travels down one leg
- Pain that worsens with sitting and quickly improves while walking
- Pain that is noticeably worse in the morning
“Typically, a person experiences some combination of these symptoms, which can develop suddenly or over time. In some cases, lower back pain can feel like it comes and goes flaring up now and then, but generally getting progressively worse over time,” explains Dr. Palmer.
Speaking of the various causes of lower back pain…
Diagnosis Of Back Pain In Teens
Diagnosis of teenage back pain is done by taking the medical history, physical examination of the back, imaging and laboratory tests.
Read Also: Will Naproxen Help Back Pain
Types Of Abdominal Pain In Teenagers
The intensity and location of the abdominal pain indicates the types of abdominal pain .
- Generalized pain: The pain is in more than half of the abdominal area. This type of pain may be associated with indigestion, gas, or a viral infection. Sometimes, generalized pain could become severe, thus indicating blockage or other severe problem in the intestines.
- Localized pain: This pain is restricted to one part of the abdomen. It is usually associated with problems in one organ, such as stomach, gallbladder, or appendix.
- Cramping or cramp-like pain: Generally, this pain does not indicate a serious problem. It may be because of bloating or gas and might be followed by diarrhea. Cramp-like pain can be worrisome if it is accompanied by fever, occurs frequently, or lasts more than 24 hours. Women can also experience this type of pain during menstrual periods.
- Colicky pain: This pain usually starts and ends suddenly, occurring in a wave-like pattern. Usually severe in intensity, this type of pain may be associated with kidney stones or gallstones.
Radiographic And Laboratory Studies
Generally, children and adolescents without significant physical findings, short duration of pain, and a history of minor injury can be treated conservatively without radiographic or laboratory studies.5,10,11 However, patients with more concerning physical findings or history should receive plain radiography of the affected area.14,24 Anteroposterior and lateral views are often sufficient, although oblique views are useful in screening for spondylolysis.31
If the radiographic findings are normal, magnetic resonance imaging , computed tomography , or bone scanning may be performed, depending on the concern of the physician. MRI is particularly useful for detecting tumors, infections, and disk herniations. However, performing an MRI in young children often requires general anesthesia. A bone scan may be a reasonable alternative the sensitivity of a bone scan is low , but specificity is fairly high .39 Bone scanning may not identify all bone tumors, soft tissue tumors, or soft tissue infections. A CT scan shows bone architecture and soft tissues but does not give a good view of marrow elements. CT scans generally do not require sedation or anesthesia because they can be performed quickly. When oblique radiographic findings are normal and spondylolysis is suspected, CT or MRI may be performed.40
An algorithm for the evaluation and treatment of children and adolescents with back pain is presented in Figure 4.24,41
Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Read the full article.
Recommended Reading: Aleve Or Advil For Back Pain
Who Should I See For Lower Back Pain
Your primary care physician knows you best and should be your first contact for lower back pain. If he or she is unable to diagnose or treat the issue, you may get referred to a specialist, such as a rehabilitation physician . These specialists practice a comprehensive approach to lower back pain, and can diagnose and treat a variety of conditions that have lower back pain as a symptom.
Later, you may get referred to a physical therapist, a chiropractor or another practitioner depending on the nature of your back pain. The good news is that surgery is rarely needed for lower back pain. Only about one in ten patients needs lower back surgery, Chhatre says.
Evaluation Of Back Pain In Children And Adolescents

ROBERT M. BERNSTEIN, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California
HAROLD COZEN, MD, Palos Verdes Estates, California
Am Fam Physician. 2007 Dec 1 76:1669-1676.
Back pain is fairly prevalent in healthy children and adolescents. When children or adolescents seek medical care for back pain, it is highly likely that underlying pathology will be identified. Common causes of back pain include nonspecific pain or muscle strain, herniated disk, spondylolysis, scoliosis, and Scheuermann’s kyphosis. Less common causes include tumor, infection, and sickle cell crisis. If nonspecific back pain is suspected, treatment may include home-based exercise, physical therapy, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If the history and physical examination suggest underlying pathology, radiography, complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and a C-reactive protein measurement should be performed. Follow-up magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, or bone scanning may be needed depending on the suspected cause. It is generally accepted that the following factors warrant immediate evaluation: patient age younger than four years, persistent symptoms, self-imposed activity limitations, systemic symptoms, increasing discomfort, persistent nighttime pain, and neurologic symptoms.
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
SORT: KEY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR PRACTICE
Read Also: Is Aleve Good For Lower Back Pain
Lower Abdominal Pain In Teenage Girls
A few causes of abdominal pain are specific to teenage girls .
Back Pain And Schoolbags
A heavy bag slung over one shoulder can, over many years of schooling, cause chronic back problems that linger into adulthood. Risks include muscle strain, distortion of the natural S curve of the spine and rounding of the shoulders.
Parents and carers can reduce the risk of schoolbag-related back problems by making sure their child has an appropriately sized backpack and a load that isnt too heavy.
You May Like: Tylenol Or Aleve For Back Pain
Medical Conditions That Can Cause Back Pain In Children
Always see your doctor for diagnosis if your child complains of ongoing back pain, particularly if it wakes them at night or is associated with long periods of stiffness in the morning. Soft tissue injuries are the most likely cause, but in some cases the pain is caused by medical conditions that require professional treatment. These can include:
- injuries to bones and joints such as compression fractures and disc injuries these are rare in children
- fibromyalgia although more common in adults, this chronic pain disorder does occur in adolescents, causing back and neck pain, with muscle spasm and fatigue
- sciatica pain radiating down the buttock and leg, caused by compression of the sciatic nerve this is rare in children
- Scheuermanns disease a growth disorder of the vertebrae in adolescents, which may produce a humpback curvature
- idiopathic scoliosis sideways curvature of the spine with an unknown cause. It is usually not painful. Any persistent pain associated with a fixed curvature must be carefully investigated
- spondylosis a congenital structural defect in the vertebrae. Certain activities may increase the potential for pain .