Lower Left Back Pain In Teenage Girl
You might really feel like relaxing, but moving is good for your back. Workouts for lower pain in the back can strengthen back, belly, and also leg muscular tissues. They aid support your spinal column, relieving pain in the back. Lower Left Back Pain In Teenage Girl
Constantly ask your health treatment specialist prior to doing any exercise for pain in the back. Depending on the reason and also intensity of your suffering, some exercises might not be recommended and can be harmful.
There are various kinds of back pain.
Back pain can be acute or chronic. It can seem like an unexpected, sharp pain or a blunted, constant pains.
Acute back pain lasts from a few days to a few weeks. Its commonly triggered by a crash, loss, or raising something thats also hefty. Acute pain in the back usually gets better by itself, without any treatment. However there may be times when you require to get healthcare.
Chronic lower back pain lasts for more than 3 months. Its a lot less typical than acute pain in the back. The majority of persistent pain in the back can be dealt with without surgical treatment.
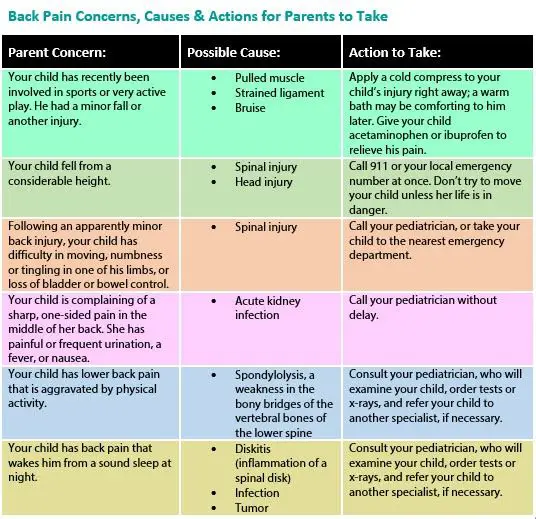
Warning Signs To Know
Every parent whose child is complaining of back pain worries that a more serious problem may be occurring. While there are certainly serious causes of back pain, the vast majority of kids with back pain have symptoms that result from muscle or ligament injury, without any structural abnormality.
Some of the back pain warning signs to look out for more serious problems include:
- Night pain
- Constant symptoms of pain
- Symptoms of generalized illness
- Symptoms persisting beyond several weeks
- Symptoms in very young children
- Leg pain, numbness, or weakness
These warning signs don’t necessarily mean there is a more serious problem, however, they are a good screening test to determine if more evaluation should be pursued. For example, muscular back pain can persist for months, however, if the symptoms have been going on for several weeks, it’s best to ensure the diagnosis is clear.
Lbp Without Related Pathology
For the majority of adolescents, LBP has no clear pathoanatomical basis, leaving a diagnostic and management vacuum. This vacuum is often filled by common beliefs with regard to the underlying basis of LBP. Some view LBP as a normal life experience during adolescent development that is not disabling and should not be given attention. While this is the case for some adolescents who have LBP that is transient and nondisabling, for a substantial number of adolescents, LBP has a profound and growing impact., Diagnostic labels commonly considered to be related to LBP include hypermobility syndromes, postural syndromes , muscular imbalances, and overuse disorders, in which LBP is provoked by sport participation. Clinical advice is often provided to avoid or minimize specific sports, wear special backpacks or minimize their use, and adhere to specific exercise and postural correction programs.
While some of these labels are clinically appealing, the evidence underpinning them is largely limited. Our group has investigated the relationship between a number of these different factors and LBP in adolescents, outlined as follows.
Read Also: Is Aleve Good For Lower Back Pain
Causes Of Abdominal Pain In Teens And Ways To Treat It
The abdominal region includes the most vital organs of the body, like the stomach, liver, intestines, and pancreas. Abdominal pain is often an indicator of a problem in these organs or the groin.
Abdominal pain or stomach ache is often not a serious ailment, and children, including teenagers, experience it at some point. However, severe and recurrent pain accompanied by other symptoms will require medical attention. In this post, we present the various reasons behind abdominal pain in teenagers, along with the treatment options.
Home Care Tips To Manage Abdominal Pain
If your child experiences abdominal pain with other symptoms, it is advised to visit a healthcare practitioner to identify the cause of abdominal pain. Do not give any over-the-counter medicine to your child without talking to your doctor. However, for mild abdominal pain, you may try the following tips at home to relieve pain .
- Sip water: Keep slowly sipping water or other fluids. Warm liquids may help relieve pain.
- Avoid solid food: Avoid solid food or food that is hard to digest for the first few hours or till you see your doctor.
- Eat specific food items after vomiting: If the teen has been vomiting, then avoid consuming solid food for at least six hours. You may give your child mild food items such as rice, apple juice, or crackers. Do not give your child dairy products.
- Avoid citrus food items during indigestion: If your child is experiencing heartburn or indigestion with pain in the upper part of the abdomen, then avoid citrus, greasy, or fatty foods. You may also avoid tomato products, caffeine, and carbonated drinks.
Don’t Miss: Does Aleve Help Back Pain
Vacuuming Lower Back Pain In Teenage Girl Athletes
When it pertains to reinforcing the lower back, concentrating on your transverse abs which are twisted around the midline of your body is one of the most effective methods to do it. These muscular tissues are actually key in sustaining your spinal column and also lower back. While individuals commonly towards crises for their transverse abdominals, people can accidentally throw away their lower back if their core isnt solid enough.
Exactly how to do it: In a standing setting, take a deep breath as well as attract your belly button in towards your spinal column, contracting and also involving your ab muscle mass as you do so. Envision if a person was mosting likely to turn up and punch you in the stomach and you desire your intestine to be difficult and also able to take it thats what it should feel like. Hold it, and also release slowly. Repeat a few even more times.
What Can Cause Back Pain In Teens
- Common Causes of Back Pain in Teens: The general cause of back pain in teenagers and children is due to muscular sprain and strain resulting from:
- Poor posture 2
- Sedentary life style, continuously sitting in front of the computer or watching television tends to cause back pain in children.
- Carrying heavy school bags can also cause teenage back pain
- Injuries caused during sports activities.
The severity of back pain in teens in the above mentioned cases varies and it may be sharp and shooting, burning, aching and felt anytime in the back.
You May Like: Mayo Clinic Low Back Pain Exercises
What Is The Anatomy Of The Lower Back
To recognize different sources of lower pain in the back, it is very important to value the normal design of the cells of this location of the body. Vital structures of the lower back that can be connected to signs in this area include the bony lumbar spine , discs in between the vertebrae, ligaments around the spine as well as discs, spine and nerves, muscular tissues of the lower back, inner organs of the pelvis and also abdominal area, and the skin covering the back area. Lower Back Pain In Teenage Girl Athletes
The bony lumbar back is made so that vertebrae piled with each other can provide a movable support structure while likewise securing the spine from injury. The spinal cord is composed of worried cells that extends down the spinal column from the brain. Lower Back Pain In Teenage Girl Athletes
Each vertebra has a spinous procedure, a bony prominence behind the spinal cord, which shields the cords worried tissue from effect trauma. Backbone also have a solid bony body in front of the spine to supply a system ideal for weight bearing of all tissues over the buttocks. The lumbar vertebrae pile quickly atop the sacrum bone that is positioned in between the butts.On each side, the sacrum meets the iliac bone of the pelvis to develop the sacroiliac joints of the butts.
Where You Take Them Matters
Learn more about our spine specialists who are dedicated to treating kids and teens, or request an appointment with our team of experts for a diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan for your child.
There are multiple factors a pediatrician should consider when determining if your child needs to be referred to a pediatric spine specialist. These may include:
- Back pain resulting in stiffness of the spine and associated with a fever, general discomfort, uneasiness or pain, or a poor appetite
- Chronic pain that lasts longer than six weeks
- Back pain associated with leg pain
- Back pain that interferes with your childs sleep
- Back pain that prevents your child from participating in activities
Recommended Reading: Mayo Clinic Lower Back Pain Exercises
What Does This Epidemiological Evidence Tell Us About Adolescent Lbp
Low back pain is common in adolescents, and for a sizable group this is associated with a growing burden of disability and health care seeking, representing an emerging health disorder that for many tracks into adulthood. Adolescent girls carry a greater burden of impact related to LBP. Ironically, the factors that we have historically thought to be important predictors of LBP, such as carrying school bags, generalized joint hypermobility, scoliosis, poor posture, and back muscle endurance, are not strong predictors of adolescent LBP with impact. Rather, the emerging evidence suggests that the factors associated with LBP in adolescence are complex and multidimensional .
Prevention Of Back Pain In Teenagers & Children
Back pain is becoming common among teenagers and children. In majority of the cases, it is caused by muscular sprain and strain and gets treated with some variations in daily activities. Due to advent of medical technology, today, teenage back pain can be managed very well so that they can live a better life in the future.
Advertisement
Read Also: Ibuprofen For Back Pain Dosage
How Is Back Pain In Children Treated
Fortunately, it is very uncommon for a child to need surgery for back pain.
Research and experience show that a daily exercise program can greatly reduce your child’s back pain. Our team connects you with the best provider to manage your childs pain and arrange more tests, if needed.
If your childs back pain doesnt improve, your doctor may refer you to the Pain Clinic at Children’s Colorado where pain specialists will work together to help your child.
When Should Children And Teens See A Doctor About Back Pain

Contact a doctor if back pain does not improve within three weeks. Younger children who experience back pain with no known history or recent injury should be examined by their pediatrician sooner rather than later.
“The best thing to do for children or teens with back pain is to see your child’s pediatrician or family practitioner,” says Dr. Smurawa. “They can treat a lot of simpler injuries or conditions, and if needed, refer your child to a specialist.”
If your child experiences fever or a rash with back pain, contact your pediatrician immediately. These may be signs of a more serious injury or infection.
Read Also: How Much Advil For Back Pain
Remain Solid Lower Back Pain In Teenage Girl Athletes
When your lower back pain has actually receded, you can aid avoid future episodes of back pain by functioning the muscle mass that sustain your lower back, consisting of the back extensor muscles. They help you preserve the correct pose and positioning of your spinal column. Having strong hip, pelvic, and stomach muscles also provides you extra back support. Prevent abdominal crises, due to the fact that they can really put more pressure on your back.
Examining Back Pain In Kids
Your childs doctor will first complete a physical examination of your child, which may include physical movements like bending to touch toes or twisting, and will ask several questions to determine the cause and location of the pain. Your childs doctor may also recommend additional tests, such as:
Once our pediatric spine specialists determine the specific injury or cause of your childs back pain, we may suggest treatment. Below are examples of treatment based on common sources of back pain in children:
Also Check: How Much Advil For Back Pain
Causes Of Back Pain In Children
While a single incident can cause sudden spinal injury, cases of nagging, ongoing back pain seem to be caused by a range of factors working in combination. Relatively minor injuries as a result of normal sports and games may lead to muscle spasm, so some back muscles may have to work harder than others. This can cause fatigue, pain and changes in posture. Poor posture can further contribute to back pain. A child with a sore back may avoid sporting activities, and the lack of exercise may then cause further problems.Many things can lead to back pain in children, including:
- gender back pain is more common in females
- age children at 12 years and over experience significantly more back pain than younger children
- obesity and poor posture
- heavy schoolbags carried on one shoulder or in one hand
- incorrectly packed backpacks
- sedentary lifestyle, such as watching a lot of television or sitting or lying down in front of the computer
- injuries caused by vigorous sports such as football or horseriding, flexibility-dependent sports such as gymnastics or dance, and power sports such as weightlifting or rowing
- soft tissue injuries, such as strains and sprains
- competitive sports that demand intense training for example, tight thigh muscles can trigger lower back pain.
Correct Backpack Lifting And Carrying Techniques
To reduce your child’s risk of injury when using a backpack:
- Adjust the shoulder straps so that the bottom of the backpack is just above the childs waist dont allow them to wear the backpack slung low over their buttocks.
- Make sure that the backpack is fitted correctly it should follow the shape of the childs back, rather than hang off their shoulders.
- Teach your child to:
- lift the backpack with a straight back, using their thigh muscles
- lifted the backpack with both hands, holding it close to their body
- slip an arm through one shoulder strap, and then the other.
Read Also: Tylenol Or Aleve For Back Pain
Diagnostic Tools And Assessment
Past studies have suggested that children with low back pain likely suffer from serious spinal pathologies, such as infections and tumors. These studies provided the evidence for the extensive diagnostic workup of pediatric low back pain practiced today.
However, recent epidemiological evidence has indicated pediatric low back pain may be much more prevalent than previously perceived and often mechanical in nature. As a result a far greater emphasis is being placed on conducting a thorough subjective history and physical examination, before performing costly and often inconclusive diagnostic tests.
The subjective history should include:
- Posture, pelvis heights, lower limb alignment, foot arches, skin markings are observed with the patient standing
- Lower limb lengths and alignment can be assessed in supine or sitting position
Range of Movement
Reproduction of symptoms, quality of movement and resistance should be observed.
- Active movements of the spine should be tested in a standing position with the pelvis/iliac crest stabilized
- Passive physiological intervertebral movements of the spine can be performed in side lying/ supine/ sitting to assess the range of movement at each segment of the spine
- Passive accessory intervertebral movements can be performed in supine/ prone as required
Resisted Isometric Movements
The following resisted movements should be performed with the spine in a neutral position
Provided neutral testing is normal further testing can be performed: