What Is Adult Scoliosis
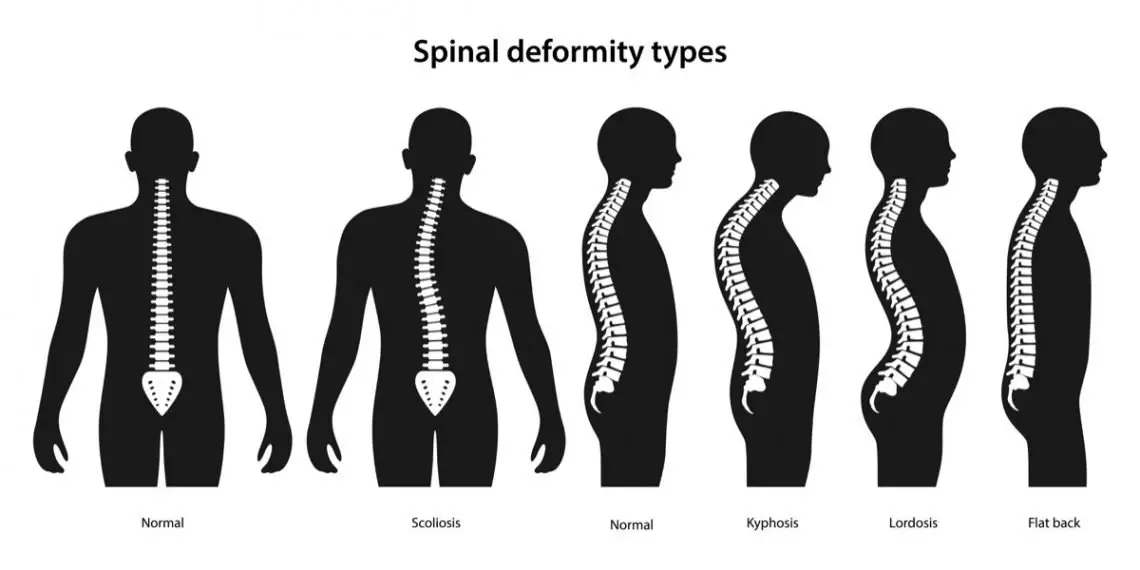
Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine . There is a natural, forward-and-backward curve to the spine. With scoliosis, the spine rotates and develops a side-to-side curve. Curves may be as mild as 10 degrees, or as severe as 100 degrees or more.
Most cases of scoliosis are mild and dont need treatment. In adults, the degree of the spinal curve may or may not determine treatment. Treatment is geared towards relieving symptoms, and not necessarily fixing the curve. The goal is always to decrease pain and improve function.
Though scoliosis itself is painless, the normal age-related degeneration of the spine may lead to symptoms. These symptoms are treated the same whether there is scoliosis or not. Scoliosis only becomes a factor when surgery is being considered. Changes in the appearance of the body are also possible depending on the degree of the spinal curve.
In general, most scoliosis in adolescents occurs in the thoracic or rib cage portion of the spine. In adults the main concern is typically in the lumbar or lower spine. This portion of the spine is most susceptible to the changes seen with aging or degeneration.
Surgery In Teenagers And Young Adults
In teenagers and young adults whose spine has stopped growing, an operation called a spinal fusion may be carried out.
This is a major operation where the spine is straightened using metal rods attached with screws, hooks, and/or wires, and bone grafts are used to fuse the spine in place. This metalwork will usually be left in place permanently, unless they cause any problems.
The surgery will take several hours. After surgery, your child will be transferred to an intensive care unit or high dependency unit , where they will be given fluids through a vein and pain relief. Most children are well enough to leave intensive care after a day or two, although they will often need to spend another five to 10 days in hospital.
After the operation, most children can return to school after a few weeks and can play sports after a few months. Contact sports should be avoided for 9-12 months. Occasionally a back brace may need to be worn to protect the metal rods after surgery.
Muscle Degeneration At The Local Level
An August 2021 paper in the Global Spine Journal investigated the effect of paraspinal muscle degeneration in degenerative lumbar scoliosis cases where patients had corrective surgery. In this study:
- 98 degenerative lumbar scoliosis patients were examined through an average 38.3 months follow-up after corrective surgery.
- The T1 pelvic angle, lumbar lordosis, and pelvic incidence were measured preoperatively, immediately postoperatively, and at last follow-up.
- Patients were divided into the lumbar lordosis maintenance group and the lumbar lordosis loss group .
- Explanatory note. Lumbar Lordosis Loss or Flat Back Syndrome has been described for decades. In 1988 Dr. Michael O. LaGrone wrote in the journal The Orthopedic clinics of North America: Symptomatic loss of lumbar lordosis is a disabling complication of scoliosis surgery. This so-called flat-back syndrome is characterized by an inability to stand erect and by upper back pain. Distraction instrumentation extending into the lower lumbar spine or sacrum is the most frequently identified etiologic factor responsible for loss of lordosis.
Don’t Miss: Is Aleve Or Ibuprofen Better For Back Pain
How Is Adult Scoliosis Pain Treated
Because each person is unique, a customized treatment plan is recommended to reduce curvature, improve functionality, and relieve scoliosis pain in adults. It is also important to address the conditions underlying cause bone mass and density loss with nutrient supplements and possibly hormone replacement therapy.
Other non-surgical scoliosis treatment options include balancing and isometric exercises, Automatic Response Training exercises, ScoliSMART Activity Suit, and nutritional testing.
Request More Information
Rates Of Idiopathic Scoliosis Rise Dramatically With Age
A 2014 review published in American Family Physician found that approximately 85% of scoliosis cases are classified as idiopathic, or of unknown cause.1 So, 85% of the people who get diagnosed with scoliosis get no explanation as to what has caused it.
The same review found that between 2% and 4% of teenagers have scoliosis. According to a retrospective study done at Johns Hopkins University, the rate of scoliosis increases to more than 8% in adults over the age of 40.7 And a 2005 study of 75 healthy adults over the age of 60, with no previous diagnosis of scoliosis or spinal surgery, found the rate of scoliosis to be 68%.8
This increasing prevalence with age is a strong indicator that muscular contraction from repetitive activities, injury, and stressthe effects of which increase with ageplay a role in developing the condition.
Also Check: Does Aleve Help Lower Back Pain
Sensations That Might Indicate A Medical Emergency
1. Sharp pain rather than a dull ache: This could indicate a torn muscle or ligament, or a problem with an internal organ in the back or side.2. Radiating pain: This pain “moves” or shoots to the glutes or legs, which could indicate a nerve compression condition.
3. Sudden weakness in the legs: Limb weakness can be caused by compressed nerves in the spine due to conditions like sciatica or spinal stenosis. However, sudden leg weakness could also indicate a stroke.4. Incontinence: Back pain paired with inability to control the bowels or bladder might be a sign of serious nerve compression or a spine infection, such as discitis or meningitis.5. Numbness or pins and needles in the groin or glutes: This is known as saddle anesthesia and is also a sign of a serious nerve or spine condition.
If you have leg weakness, incontinence, and numbness together, you might have cauda equina syndrome, a serious illness characterized by spinal cord nerve damage. This is a medical emergency, and patients usually need surgery immediately to decompress the nerves and reduce permanent damage.
Related reading: Get help for back, neck, and leg pain caused by spinal stenosis
How Is Degenerative Scoliosis Diagnosed
An orthopedic surgeon will get the patient’s history, conduct a physical exam and order full spine images, low-dose radiation images or, in some cases, a to confirm a diagnosis for degenerative scoliosis.
These images will be taken of the full spine from both the front and from the side. EOS imaging allows these to be taken simultaneously, without requiring the patient to reposition. CT scans can can provide additional detail, including evidence of arthrosis of the facet joints or the presence of small spinal fractures that may not be visible on X-ray images.
Figures 1 & 2: X-rays showing degenerative scoliosis in its first stages and in a more progressive case .
Figure 3 : CT scan showing normal facet joints with a green arrow pointing to the smooth and regular joint surfaces. Figure 4 : CT scan showing abnormal, osteoarthritic facet joints with thinned and irregular joint surfaces and bone spurs .
may also be used to obtain information about the nerves, discs, and soft tissue in the spine. This is particularly helpful in determining the cause of radicular symptoms in the legs.
Figure 5 : MRI of a patient with a facet cyst causing compression of nerves. Figure 6 : MRI of same patient after facet injection and cyst rupture , completely relieving the compression and eliminating the patient’s pain.
Read Also: How Does A Diuretic Help Back Pain
The Secret Source Of Back Pain
Is that back pain not going away? More than half of Americans will experience some form of back pain. For a small amount, the source can be scoliosis. Scoliosis affects about 6-9 million adolescents and adults. With the right treatment, including surgery, doctors can help reduce that chronic back pain.
Scoliosis Pain: Understanding Your Treatment Options
If youve found this page, chances are you or a loved one are experiencing scoliosis pain. Youve come to the right place. I have over 30 years of experience treating scoliosis and over the years have helped thousands of patients alleviate their scoliosis pain.
In this article, Ill explain
- Why scoliosis causes pain
- The most common types of scoliosis pain
- Popular methods for treating scoliosis related pain
- Strauss Scoliosis Corrections unique approach to treating pain.
- 3 exercises you can try today to start alleviating pain.
You May Like: Advil Or Aleve For Back Pain
How Can Adult Scoliosis Affect The Legs
In adults, scoliosis is an acceleration of the agingprocess in the spine. As the tissue degenerates, the spine begins to curve intoa C-shape instead of the classicS-shaped curve of idiopathic scoliosis. The curvature causes a spinalimbalance, making it tough for patients to stand up straight, walk, or runwithout pain.
Spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spinalcanal, is often paired with adult scoliosis. It causes compression of nerves in the spine, whichresults in shooting pain, tingling, heaviness, weakness, and numbness in the buttocksand the legs a cluster of symptoms more commonly known as sciatica.
The Cause Of Idiopathic Scoliosis: Involuntary Muscle Contraction
Scoliosis is regarded as mysterious and incurable by many people in the medical community. While some scoliosis cases are caused by congenital structural abnormalities or neurological or muscular diseases, the vast majorityaround 85%are of unknown cause.
The fact is, the bones in our body do not move unless our muscles move them. And our muscles are controlled by our nervous system. So when our vertebrae move out of alignment in any way, they are being moved by our muscles, which are being controlled by our nervous system.
Many cases of idiopathic scoliosis are caused by chronically tight muscles pulling the spine out of alignment. If you have idiopathic scoliosis, you can touch your back and waist and feel how tight your muscles are.
If your nervous system is sending messages to your muscles to stay tight, no amount of passive lengthening or forced re-alignment will change these messages.
In this post, well talk about the patterns of muscular contraction that are common in idiopathic scoliosis, how our natural motor learning process leads us to develop these patterns, and how pandiculation retrains the nervous system to release chronic, involuntary muscular contraction.
This is the best program I have encountered. I am a military veteran, with 2 tours to Afghanistan and have scoliosis which became much worse due to all the heavy lifting and carry overseas. These exercises have released the muscles and I am almost back to normal.-Alisa
Recommended Reading: Advil Good For Back Pain
What Spinal Nerves Affect Bladder
The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets of peripheral nerves: pelvic parasympathetic nerves, which arise at the sacral level of the spinal cord, excite the bladder, and relax the urethra lumbar sympathetic nerves, which inhibit the bladder body and excite the bladder base and urethra and pudendal nerves, …
What Are Risk Factors For Scoliosis
Age is a risk factor as the symptoms often begin between 9-15 years of age. Being a female increases the risk of scoliosis, and females have a higher risk of worsening spine curvature than males. Although many individuals who develop the problem do not have family members with scoliosis, a family history of scoliosis increases the risk of the disease.
Read Also: Does Aleve Help Back Pain
Natural History And Treatment
Natural history studies of patients with idiopathic scoliosis after skeletal maturity, found that curves less than 30° do not progress, while most curves of greater than 50° continue to progress. The progression is approximately 1° per year . In patients with severe thoracic curves , there is an increased risk of cor pulmonale and right heart failure. However, an increased mortality rate has not been found in long-term studies of patients with AIS. Pulmonary function can become limited with severe scoliosis . Back pain is common in the normal population, making studies evaluating back pain in scoliosis difficult. Some studies show a slightly higher rate of back pain in patients with AIS . Scoliosis has also been found to be a risk factor for psychosocial issues and health compromising behaviour . However, there have been no studies comparing treated and untreated patients with scoliosis to their rates of back pain and their self image.
The treatment of scoliosis is based on the type of scoliosis, the magnitude of the curve, the number of years of growth remaining and the patients opinion about the shape of their back. The treatment of patients with congenital-, neuromuscular- and syndrome-associated scoliosis, and those with idiopathic scoliosis younger than 10 years of age, presents a number of controversies. These patients should be treated at specialized facilities their treatment is beyond the scope of the present paper.
What Is The Outlook For Adult Scoliosis
The outlook for adult scoliosis can vary depending on the type and severity of symptoms. Non-operative treatment, with modalities such as physical therapy, a regular exercise program, and over the counter anti-inflammatory medications is always the first line of care. Maintaining an ideal body weight and maintaining a regular exercise program are excellent ways to minimize symptoms associated with adult scoliosis.
Surgical treatment of adult scoliosis can improve a patients quality of life and deal with pain connected to the condition. The results of adult spinal deformity surgery are typically very good, if done well and for the right reasons. With that said, the surgeries are associated with significant risk, and should be avoided if at all possible.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 09/25/2019.
References
Read Also: Advil Vs Ibuprofen For Back Pain
Patient Age And Postural Changes
When a person is diagnosed with scoliosis, the condition is further classified based on a number of important factors: patient age, the amount of degenerative changes to the spinal joints, age that the scoliosis was identified, curvature location, and size of the curve.
These variables help in crafting an effective and customized treatment plan, as the very nature of scoliosis necessitates an integrative and customized treatment approach. Every scoliosis is different, and each patient requires a unique plan of care.
While every case is different and the aforementioned factors can all play a role in determining how painful a condition is, generally speaking, the most important pain-related variables are patient age, the extent of the degenerative changes, and severity of postural changes.
As mentioned, scoliosis is not commonly known as painful in children and adolescents, but in adults, the experience of scoliosis-related pain is very different.
Not only can scoliosis develop at any age, there are also multiple types that can develop, and the conditions most prevalent form in children is termed idiopathic, meaning there is no single-known cause. In adults over 50 years old, we see either childhood idiopathic scoliosis in the adult, or more commonly, adult degenerative scoliosis, also known as denovo scoliosis.
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis in Adults
Degenerative Adult Scoliosis
Diagnosing Scoliosis Of The Spine
Normally, the spine contains a forward-backward curve but when the spine curves sideways, it becomes scoliosis. For a doctor to diagnose scoliosis, the Cobb angle must be greater than 10 degrees. The Cobb Angle measures the curvature of the spine. For scoliosis, this is the angle of maximum deviation from a straight spine. The condition appears during growth spurts in children between the ages of 10-15. It is referred to as Pediatric Scoliosis and at this age easily corrected and maintained to prevent progression or worsening of the condition.
When scoliosis appears after puberty, doctors refer to it as Adult Scoliosis. At this stage, the bones of the spine are completely developed and the adjustments are more limited. Depending on the Cobb Angle, scoliosis can appear as mild, moderate, or severe. Mild Scoliosis appears when the Cobb angle gets between 10 and 25 degrees. In Moderate Scoliosis, the Cobb Angle appears between 25 and 40 degrees. Angles above 40 degrees become designated as Severe Scoliosis.
Doctors can stop Mild and Moderate Scoliosis from progressing in many children and most do not usually require surgery. Patients are advised to visit their spine doctors for regular checkups to monitor the curve. X-ray images are taken and used to monitor the progression of the condition.
Severe scoliosis usually presents complications ranging from malformed posture to breathing problems. This type usually requires surgery to correct.
You May Like: Will Aleve Help Back Pain
Research: Decompressive Laminectomy For Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis Is Not Recommended Because It Can Lead To Further Instability
This is a December 2020 study published in the medical journal Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery.
Here are the learning points of this research:
Did the surgery CAUSE the instability or did the surgery fail to address the instability or both?
That is the question asked by the surgeons. Here is what they found:
- It is uncertain whether instability at the decompressed segments is directly affected by laminectomy or the natural progression of degenerative lumbar scoliosis. The purpose then of this study was to answer that question. Did the surgery cause the instability, did the surgery fail to address the instability? Both?
The surgeons then examined the case files of sixty patients with degenerative lumbar scoliosis.
- The 60 patients were divided into two groups.
- Patients with post-laminectomy instability at the point of the surgery.
- Patients with post-laminectomy instability in the adjacent segments.
One in 5 needed another surgery, one in 4 had a new instability
- This is what happened in the 60 patient groups:
- Twelve patients underwent revision surgery.
- Eleven patients showed continued post-laminectomy instability at the index segments
- and 15 patients showed post-laminectomy instability at the adjacent segments, not related to the laminectomy site.
In other words, the surgery caused it.
Here are further resources and research you can explore on our site:
What Does It Feel Like To Have Scoliosis
Rebecca P: It feels like you are stiff on one side. One side is more curvy than the other, and your legs can feel uneven.
With scoliosis, there are a lot of uneven forces at work. Feeling stiff on one side is understandable as spinal rigidity increases with curvature progression.
The muscles surrounding the spine are also worked unevenly as they try to compensate for the uneven force of the abnormal spinal curvature and support the spine.
When an abnormal curvature is present, the body becomes asymmetrical as the spines biomechanics are thrown off, and this can give the appearance, and feeling, of the legs hanging at different lengths.
Baleg D: It feels like you are being weighed down . Your body feels loose, uncomfortable, and fragile.
The feeling of being pulled down is understood as a result of the adverse tension that scoliosis introduces to the spine. A feeling of the body being pulled and stretched is a common description as the spine and the rest of the body faces the compressive nature of the abnormal curvature.
This can also affect balance and make patients feel like they cant quite get comfortable in their own bodies.
Feeling fragile has a psychological component as patients can feel concerned about the spines ability to evenly absorb and distribute force. There is also the fear of trying new activities and not knowing how the spine will react.
Tina N: It feels like lower-left back pressure that gets relief when adjusted.
Recommended Reading: How Much Advil Can I Take For Back Pain